Nebraska was founded under values of opportunity and equality for all, but when looking at the data and research on Nebraska’s children and families, a harsher reality is uncovered– one of disparity and lack of equitable chance of future success and opportunity for children of color. In response to this, the Index of Race & Opportunity for Nebraska Children was created. A composite score of 13 indicators of child well-being was calculated to highlight disparities in opportunity and measure progress toward race equity and inclusion.
7 key steps
Used to help advance and embed race equity and inclusion at all levels of policy creation
Step 1
Establish an understanding of race equity and inclusion principles.
Step 2
Engage affected populations and stakeholders.
Step 3
Gather and analyze disaggregated data.
Step 4
Conduct systems analysis of root causes of inequities.
Step 5
Identify strategies and target resources to address root causes of inequities.
Step 6
Conduct race equity impact assessment for all policies and decision-making.
Step 7
Continuously evaluate effectiveness and adapt strategies.
Indicators used include:
Health
- Children with health insurance coverage
- Infants receiving adequate prenatal care
Education
- 3- and 4-year-olds enrolled in school
- Reading proficiently at 3rd grade
- 16-24-year-olds employed or attending school
Economic Stability
- Children living above the Federal Poverty Level
- Median family income
- Children living in a low-poverty areas
Juvenile Justice
- Youth who have completed a diversion program successfully
- Youth who have completed probation successfully
Child Welfare
- Children not involved in the child welfare system
- Children who are wards of the state, but are living at home
- Children who are living in out-of-home care, but have done so in 3 or fewer placements
Children with health insurance coverage (2018)1
Infants receiving adequate prenatal care (2019)2
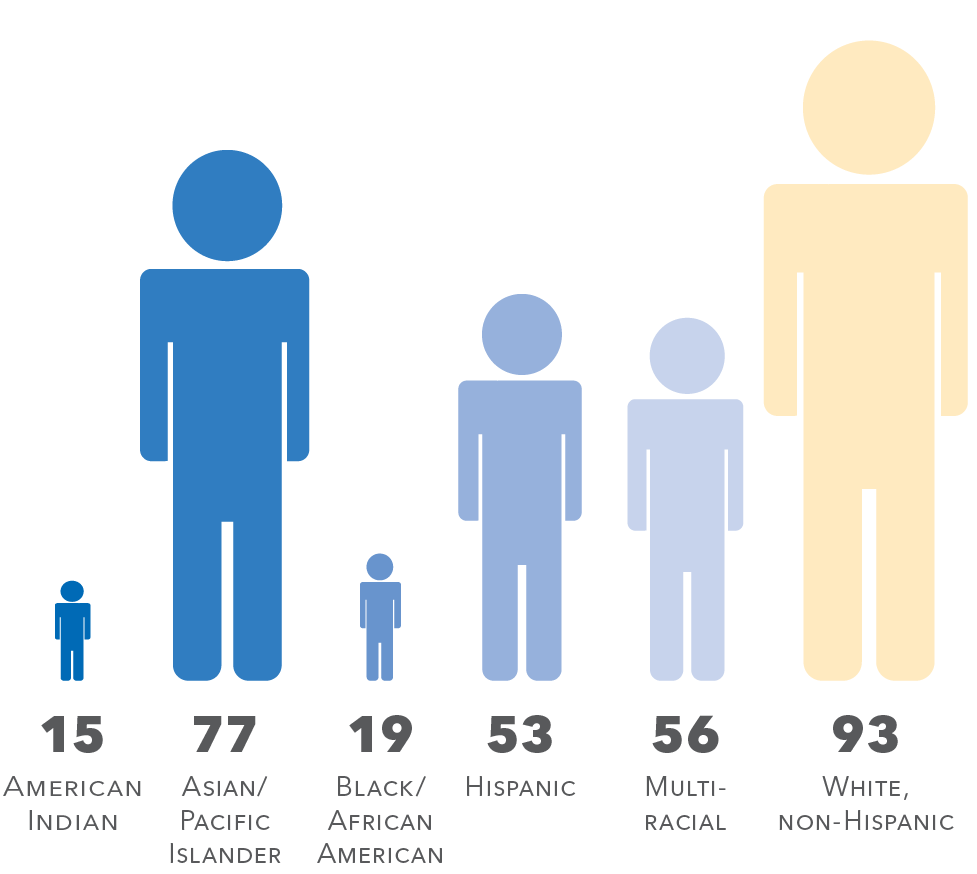
3- and 4-year-olds enrolled in school (2018)3
3rd graders reading proficiently (2018/19)4
16-24-year-olds in school oremployed (2018)5
Sources:
1. U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates, Table C27001H.
2. National Center for Health Statistics, natality data, 2019, Prepared by March of Dimes, Perinatal Data Center..
3. U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates, Public Use Microdata Samples.
4. Nebraska Department of Education, 2018/19 Nebraska Education Profile, NSCAS.
5. U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates, Public Use Microdata Samples.
Children living above the federal poverty line (2018)6
Median family income (2017)7
Children living in areas that are low poverty (2018)8
6. U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates, Table B17001I.
8. U.S. Census Bureau, 2018 American Community Survey 5-year Estimates, Table B17001H.
Youth successfully completing diversion (2018)12
Youth successfully completing probation (2018)13*
Children not involved in the child welfare system [Rate/1,000] (2018)9*
Children in child welfare system with in-home services (2019)10
Children with three or fewer out-of-home placements (2019)11
9. Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services.
* These data were calculated by dividing the number of children involved in the child welfare system by Nebraska’s total children population (18 and under) and multiplying the quotient by 1,000. These numbers were then subtracted from 1,000 to show the ratio of children not involved in the child welfare system.
11. Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services.
12. Nebraska Crime Commission, Diversion.
13. Nebraska Juvenile Probation System.
* These data were calculated by dividing the number of children involved in probation by Nebraska’s total children population (ages 11 to 19) and multiplying the quotient by 1,000. These numbers were then subtracted from 1,000 to show the ratio of children not involved in probation.

