Keeping our children and youth safe is essential to their healthy development. Children deserve to grow up in safe, permanent, and loving homes. An effective child welfare system works to strengthen families and minimize trauma through timely and appropriate action.
Families should be connected to resources in their community that strengthen their abilities to care for their children through a robust network of evidence-based services focusing on child abuse and neglect prevention that are able to meet families where they are. When children do enter the child welfare system they are entitled to retain ties to their family, culture, and community. The administration and staff of agencies should reflect the diversity of the populations they serve and work in a way that honors children’s unique heritage and cultural protective factors. Services must be trauma-informed, individualized, timely, and ongoing to maintain safety, well-being, and permanency.
Child maltreatment
Federal law defines child maltreatment, otherwise known as abuse and neglect, as “any act or failure to act that results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation, or any act or failure to act that represents an imminent risk of serious harm.”
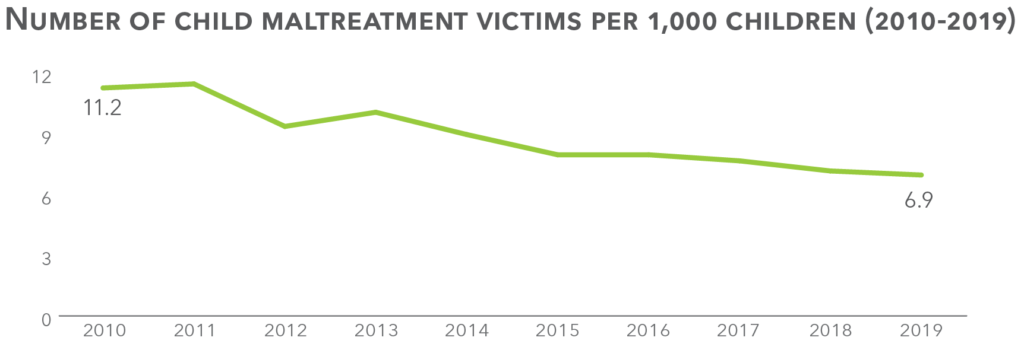
In Nebraska, the vast majority (80%) of maltreatment is physical neglect, which is a failure to meet a child’s basic needs like food, shelter, and clothing; this is, in many cases, an economic issue.
Why should we be concerned?
Exposure to childhood abuse and neglect hinders children’s healthy social, emotional, and cognitive development. If untreated, toxic stress makes it more likely that children will adopt risky behaviors which negatively impact their future health and success. Given the impacts, we need to strengthen families to prevent abuse and neglect whenever possible, and take swift, thoughtful action to ensure that all children grow up in loving homes.
Child abuse & neglect reports
37,690 reports
of alleged maltreatment were made to the Child Abuse and Neglect Hotline in 2019.
Do you know a child who is being maltreated?
Call the Child Abuse & Neglect Hotline at 1-800-652-1999.
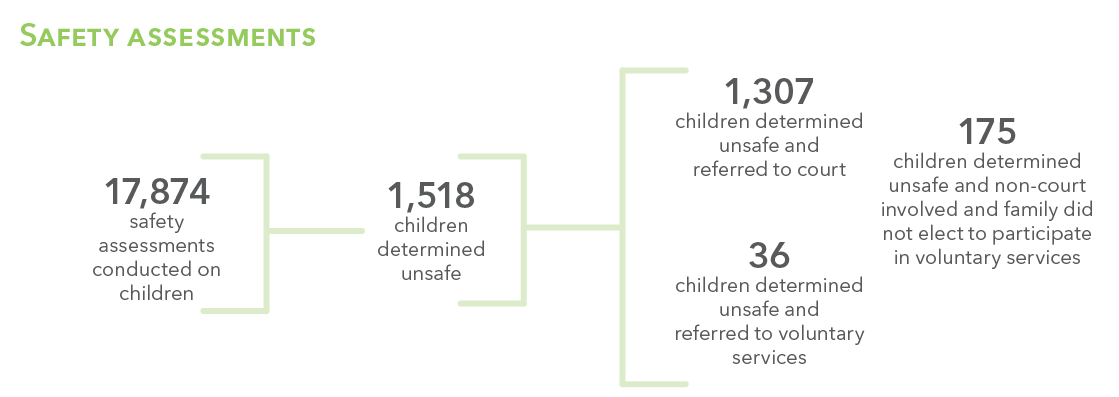
Safety Assessments
Types of substantiated maltreatment (2019)
Some children experienced more than one type of maltreatment. The numbers here will be higher than the total number of children who experienced maltreatment.
Source: Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS).
It is important to note that only maltreatment cases that were reported are included in this report. The actual incidence of maltreatment may be higher than what is reported here.
3,267 kids experienced maltreatment in 2019.
Child maltreatment by age (2019)
- Infant (0-1) (19.4%)
- Toddler (2-4) (18.0%)
- School-age (5-12) (42.2%)
- Teen (13-18) (20.4%)
- Infant (0-1) (19.4%)
- Toddler (2-4) (18.0%)
- School-age (5-12) (42.2%)
- Teen (13-18) (20.4%)
In 2019, 6,675 children in 93 counties who were alleged victims of maltreatment were served by the Child Advocacy Centers (CACs) of Nebraska.
The Nebraska Alliance of Child Advocacy Centers provides statewide leadership in the fight against child abuse alongside it’s member centers, Nebraska’s seven fully accredited Child Advocacy Centers (CACs). The CACs are located in Gering, Grand Island, Kearney, Lincoln, Norfolk, North Platte, and Omaha. There are also 10 satellite locations in other parts of the state covering each of Nebraska’s counties.
Source: Nebraska Alliance of Child Advocacy Centers.
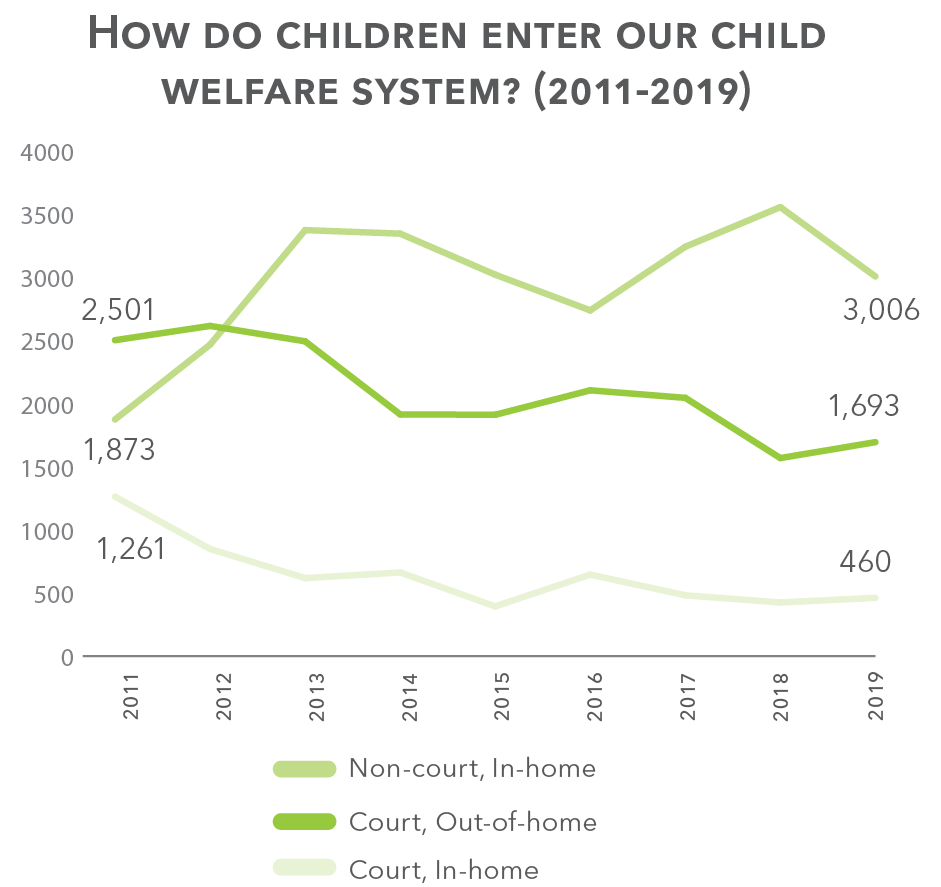
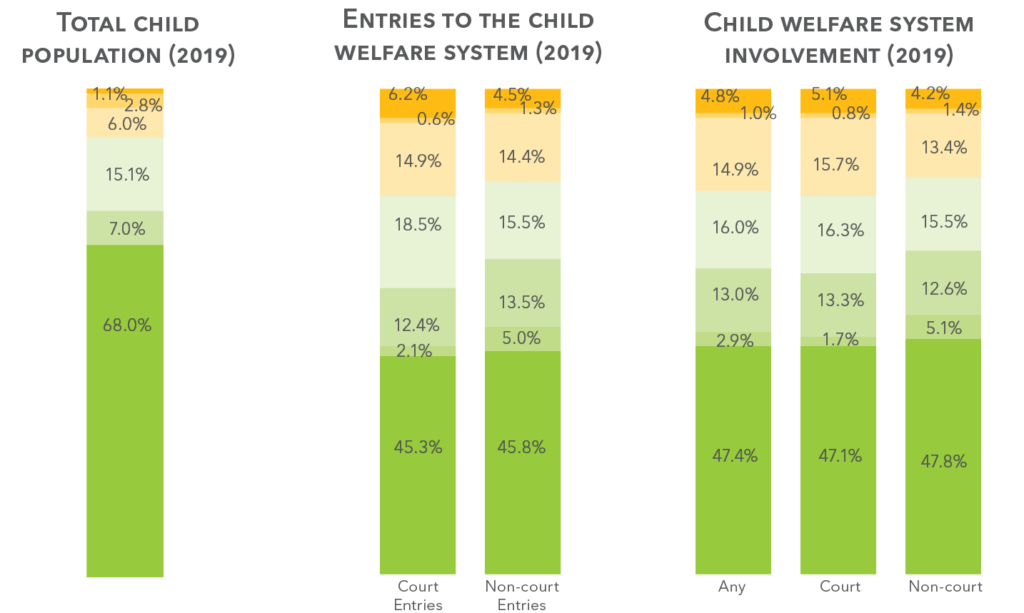
How do children enter our child welfare system? (2011-2016)
- Court, out-of-home
- Non-court, in-home
- Court, in-home
- Non-court, out-of-home
- Court, out-of-home
- Non-court, in-home
- Court, in-home
- Non-court, out-of-home
Court vs. non-court
Children who are removed from their homes often experience traumatic and long-term consequences. Recently, DHHS has been seeking ways to keep families together while ensuring that safety can be maintained. This has been reflected in data from recent years in how families enter the system, with more and more families receiving services without judicial oversight (“non-court”) when appropriate. Non-court cases allow children to remain in their own homes, where they can continue to receive a stable source of love and care from their families.
9,526 kids from 4,655 families
were involved in our child welfare system in 2019.
1,759 children entering care in 2019 had prior involvement in the child welfare system.
Entries & involvement
1,759 children entering care in 2019 had prior involvement in the child welfare system.
Any involvement by age (2019)
- Infant (0-1) (13.3%)
- Toddler (2-4) (18.8%)
- School Age (5-12) (41.2%)
- Teen (13-18) (26.7%)
- Infant (0-1) (13.3%)
- Toddler (2-4) (18.8%)
- School Age (5-12) (41.2%)
- Teen (13-18) (26.7%)
Court entries by age (2019)
- Infant (0-1) (18.6%)
- Toddler (2-4) (14.6%)
- School-age (5-12) (35.3%)
- Teen (13-18) (31.4%)
- Infant (0-1) (18.6%)
- Toddler (2-4) (14.6%)
- School-age (5-12) (35.3%)
- Teen (13-18) (31.4%)
Non-court entries by age (2019)
- Infant (0-1) (15.7%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.3%)
- School Age (5-12) (45.4%)
- Teen (13-18) (19.5%)
- Infant (0-1) (15.7%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.3%)
- School Age (5-12) (45.4%)
- Teen (13-18) (19.5%)
9,526 kids from 4,655 families were involved in our child welfare system in 2019.
Alternative Response & tribal youth
The Omaha Tribe, the Santee Sioux Nation, and the Winnebago Tribe have agreements with the State of Nebraska’s Department of Children and Family Services to provide child welfare services to tribal members within the boundaries of their reservations. These cases are under the jurisdiction of Tribal Courts and fully managed by the Tribes’ child welfare departments. The Tribal Youth data contained on this page are from DHHS and represent the services provided under those agreements.
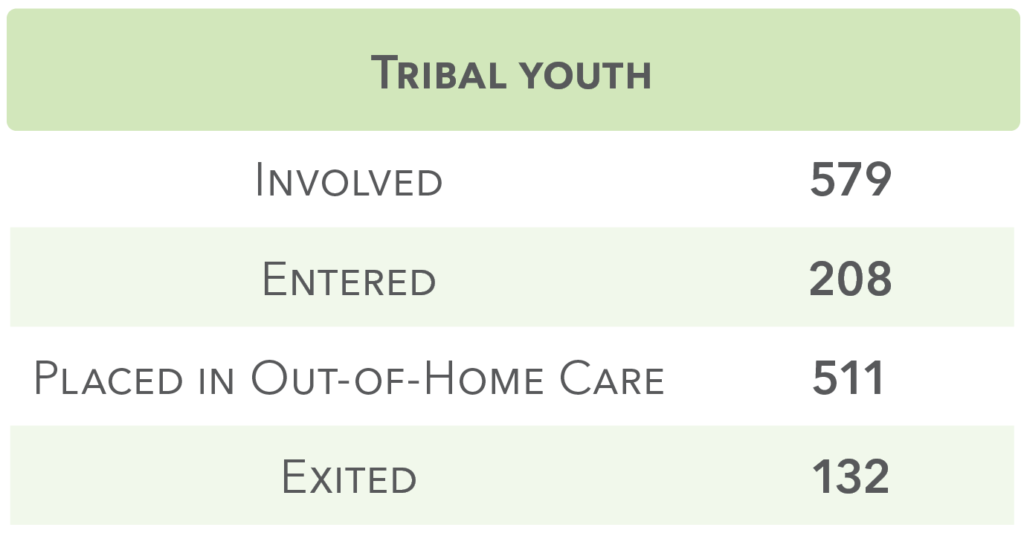
1,278 families were served by Alternative Response in 2019.
1,174 families were successfully discharged from Alternative Response in 2019.
The majority of children who come into Nebraska’s child welfare system are identified because their family is unable to meet their basic needs, which is often related to symptoms of poverty. Alternative Response brings more flexibility to our state response to child maltreatment in certain low- or moderate-risk cases by allowing caseworkers to focus on harnessing the strengths of each family and building parental capacity through intensive supports and services.
64 families changed track from Alternative Response to Traditional Response after an average 26 days of involvement.
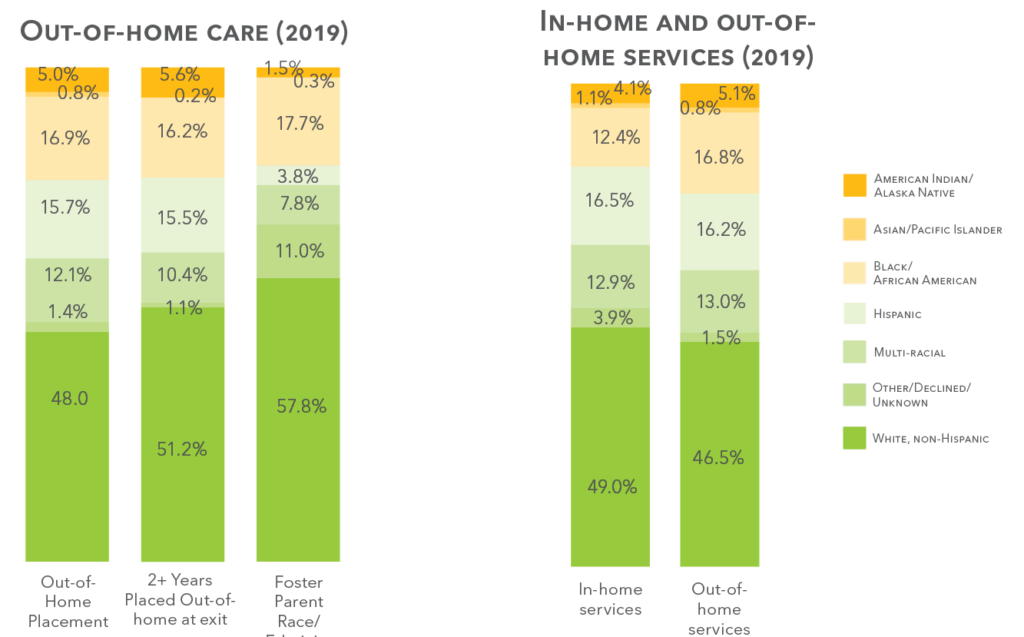
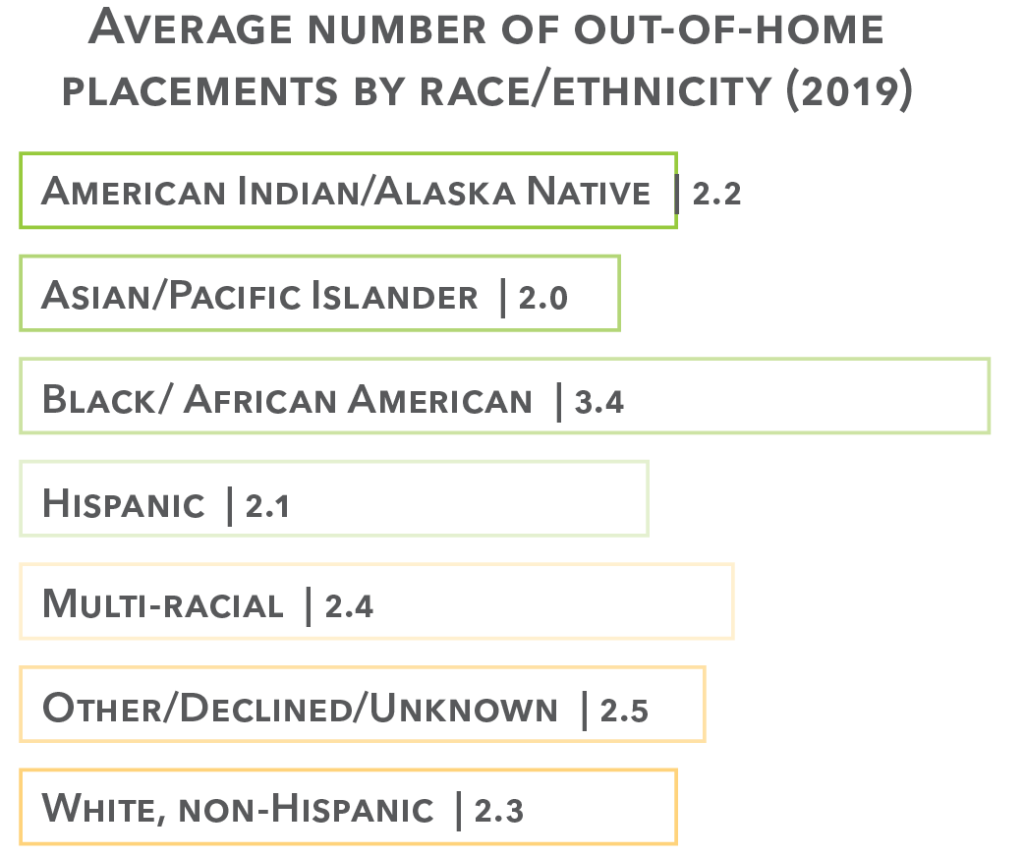
Race & ethnicity in child welfare
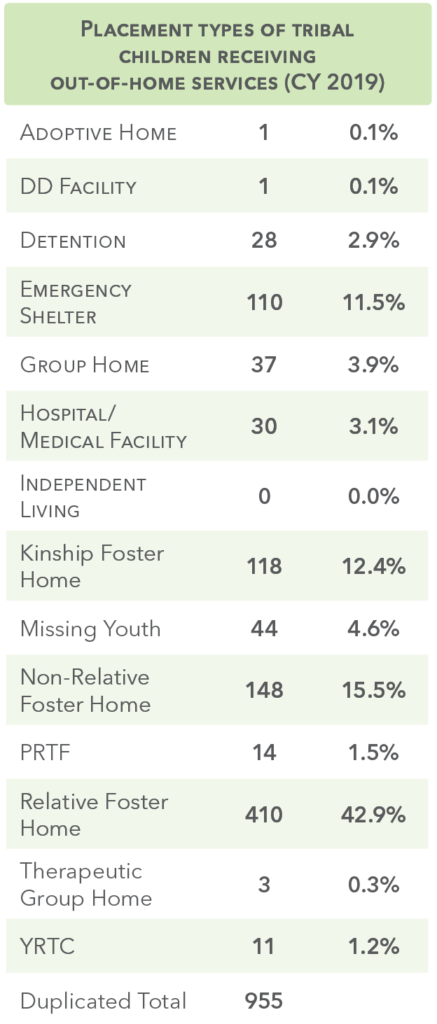
Out-of-Home Placements
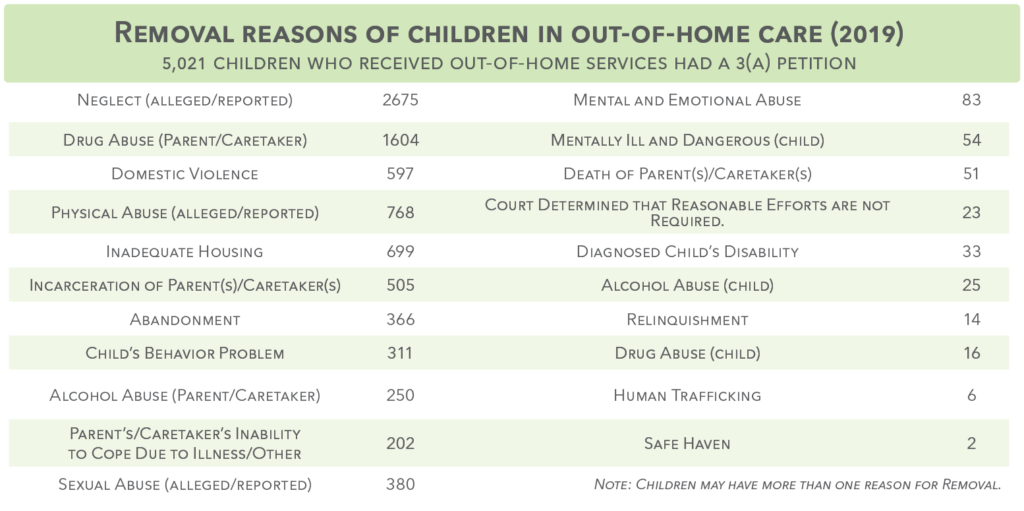
Children receiving in-home services by age (2019) TOTAL: 5,485 Children
- Infant (0-1) (13.2%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.4%)
- School-age (5-12) (46.0%)
- Teen (13-18) 798 (21.5%)
- Infant (0-1) (13.2%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.4%)
- School-age (5-12) (46.0%)
- Teen (13-18) 798 (21.5%)
Children receiving out-of-home services by age (2019) Total: 5,358 Children
- Infant (0-1) (13.8%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.0%)
- School-age (5-12) (36.3%)
- Teen (13-18) 798 (30.9%)
- Infant (0-1) (13.8%)
- Toddler (2-4) (19.0%)
- School-age (5-12) (36.3%)
- Teen (13-18) 798 (30.9%)
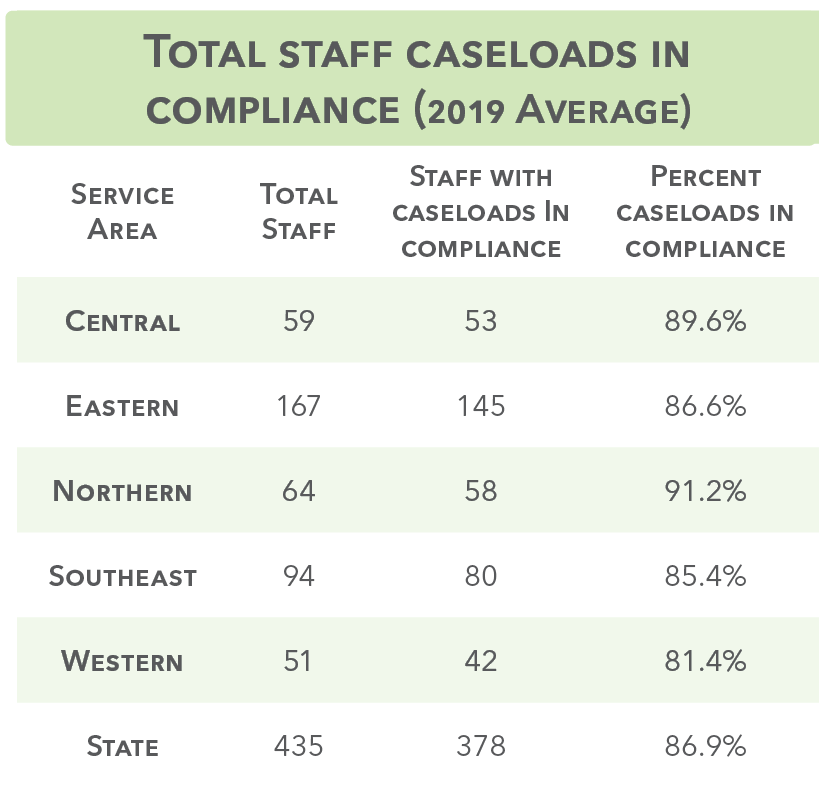
Compliance as determined by the Child Welfare League of America. There are multiple factors influencing caseload including urban or rural, initial assessment, in-home or out-of-home, and court or non-court involvement.
Out-of-home placements
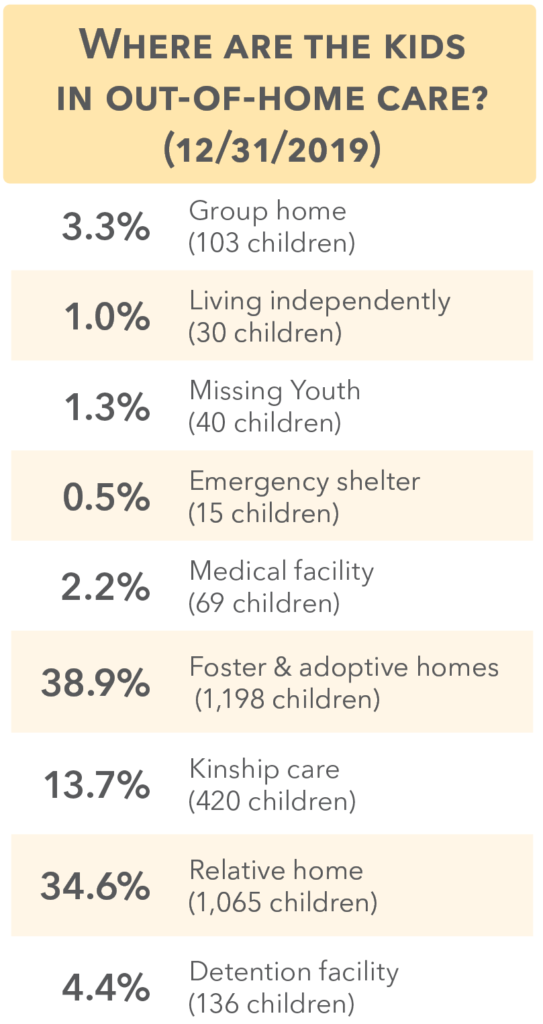
There are three types of foster parents in Nebraska:
• Relative foster homes: Foster parents who are related to the child or children whom they care for by blood, marriage, or
adoption.
• Kinship foster homes: Foster parents who have a significant pre-existing relationship with the child or children for whom they care. Examples are a current or former teacher, coach, or neighbor.
• Licensed foster homes: Foster parents who live at the licensed residence and care for a child or children whom they have not
previously known.
Foster home placement beds (12/31/2019)
5,228 licensed foster home beds were available in 2,357 homes.
1,235 approved relative or kinship beds in 722 homes.
3,993 beds in 1,635 licensed homes..
1,485 (58.3%) children in foster care in 2019 were placed with relatives or kin.
35.1% of foster home beds were in kin or relative homes.
1,987 kids in out-of-home care also had a sibling in out-of home care on 12/31/19.
- 62.8% were placed with all siblings
- 82.5% were placed with at least one sibling
2,457 kids in out-of-home care also had a sibling in out-of-home care on 12/31/16.
63% were placed with all siblings.
82% were placed with at least one sibling.
When children must be removed from their homes, it is important to ensure that their placement reduces the trauma of removal and promotes the well-being of the child. Congregate care, which places children in an institutional setting such as a group home or detention center, should be used minimally for out-of-home placements.
Research shows that placement in a familylike setting provides children with improved long-term outcomes in physical and emotional health. Although congregate care may be necessary for some children, for many others, it does not allow children to maintain the strong relationships with trusted adults that are essential for successful development.
Placement stability
Multiple placements
The Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services counts placement changes when a child moves from one foster care setting to another. Children in stable homes are reported to receive more attention, acceptance, affection, and better care from their foster parents. Children who are in stabilized homes are more likely to receive therapy, are less delinquent and oppositional/aggressive, and are more likely to be placed with competent and caring foster parents.
Source: University of Illinois, Child and Family Research Center, Placement Stability Study, 1999.
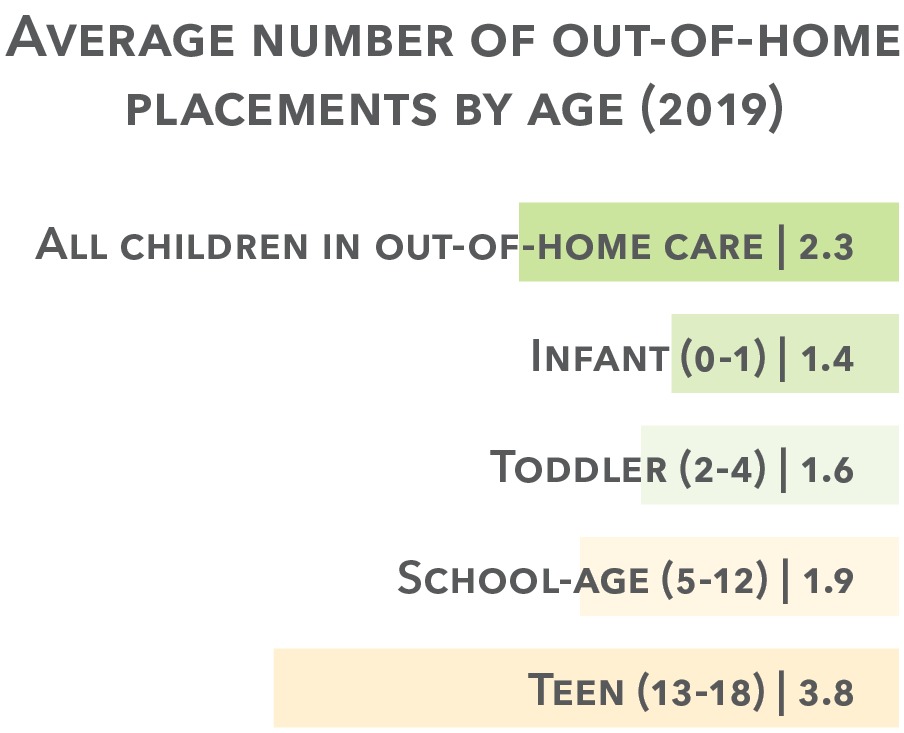
1,908 children exited out-of-home care in 2019. The mean length of time away from home was 20.2 months.
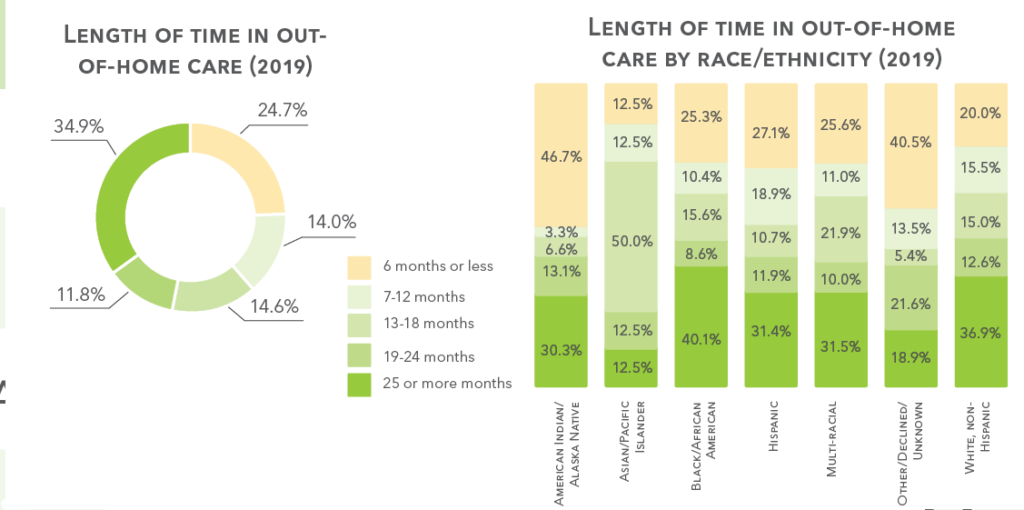
Permanency
Exiting the system
Once in the child welfare system, children should be on a track toward achieving permanency in a safe, loving environment. Most of the time that means they will be reunified with their family and return home. Other times, permanency may be achieved through adoption or guardianship.
2,687 non-court involved children exited the system in 2019.
2,465 court involved children exited the system in 2019.
223 children exited into guardianships in 2019,
204 of which were subsidized and adoptions.
549 children were adopted in 2019.
532 adoptions were subsidized. Mean time from becoming free for adoption to adoption:
10.1 months.
Exits from out-of-home care (2010-2019)
- Reunification
- Adoption
- Guardianship
- Independent Living
- Other
- Reunification
- Adoption
- Guardianship
- Independent Living
- Other
Aging Out
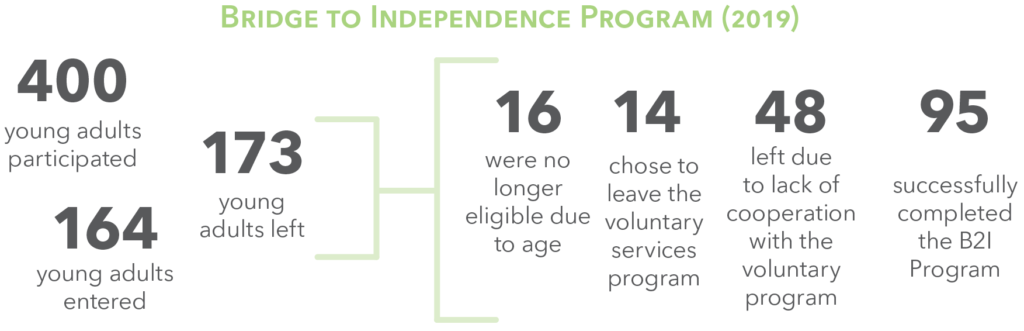
Family support is key to any successful transition into adulthood, especially for youth who may have been exposed to trauma. Learning to be self-reliant in seeking employment and housing, managing finances, or seeking healthcare can be daunting without family connections. For youth who have been in foster care who do not exit the system to a family, ensuring a strong system of support in this transition is key. The Bridge to Independence (b2i) program works to address this issue. B2i serves youth who must be either working, seeking work, or in school. In return, they receive Medicaid coverage, a monthly stipend to use for living expenses, and an assigned caseworker on call 24/7 to help them navigate the transition to adulthood.
90 youth were in out-of-home care when they reached their 19th birthday in 2019.
98.9% were HHS wards
0.0% were OJS wards
1.1% were both
101 young adults in the Bridge to Independence Program were parenting.
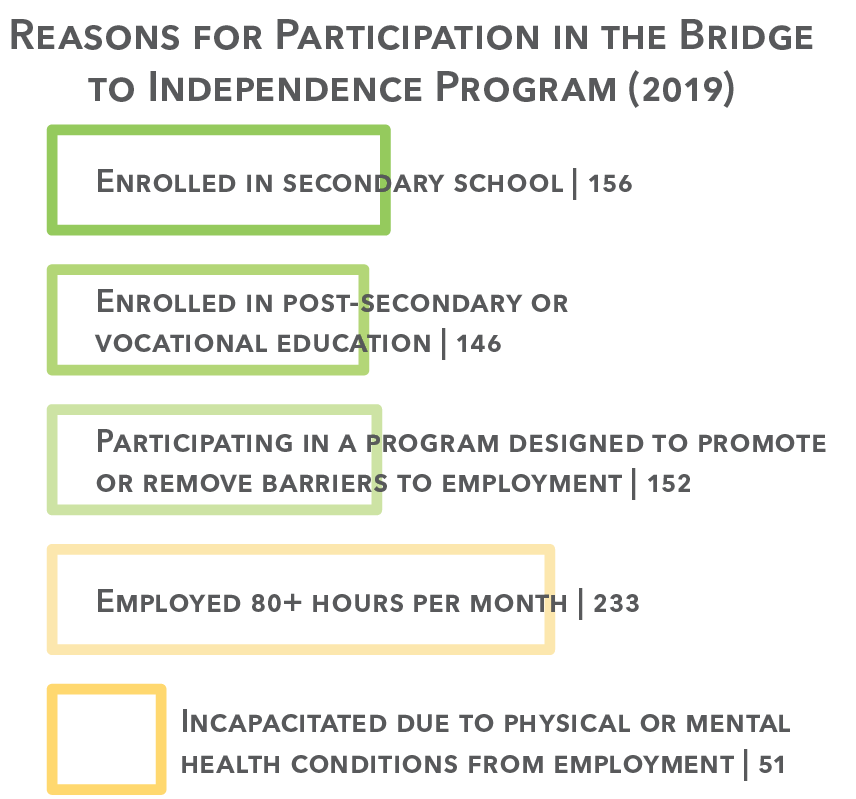
Bridge to Independence Program (2018)