Why does it matter?
A good education begins early. Access to high-quality early childhood and pre-kindergarten programs provide an important foundation for children as they move through their school years and into adulthood.
Children who are well educated are much more likely to become successful adults. Higher education is linked to higher income, higher job satisfaction, lower divorce rates, and lower crime rates. By ensuring that all children have access to high-quality educational opportunities and closing the opportunity gap we are investing in the future of our communities, our state, and our economy.
Additional supports for educationally vulnerable children— such as special education, English language learning programs, and quality alternative education programs— help ensure that children with varying needs keep pace.
82%
of Nebraska 3rd graders
score proficient or better in reading.
88.9%
of Nebraska high school students
graduated on time.
Head Start/Early Head Start
6,569
children were served by Head Start (ages 3-5) and Early Head Start (ages birth-3) in 2014/15.
132 pregnant women were served by Early Head Start in 2014/15.
Counties served by Head Start or Early Head Start grantees (2014/15)
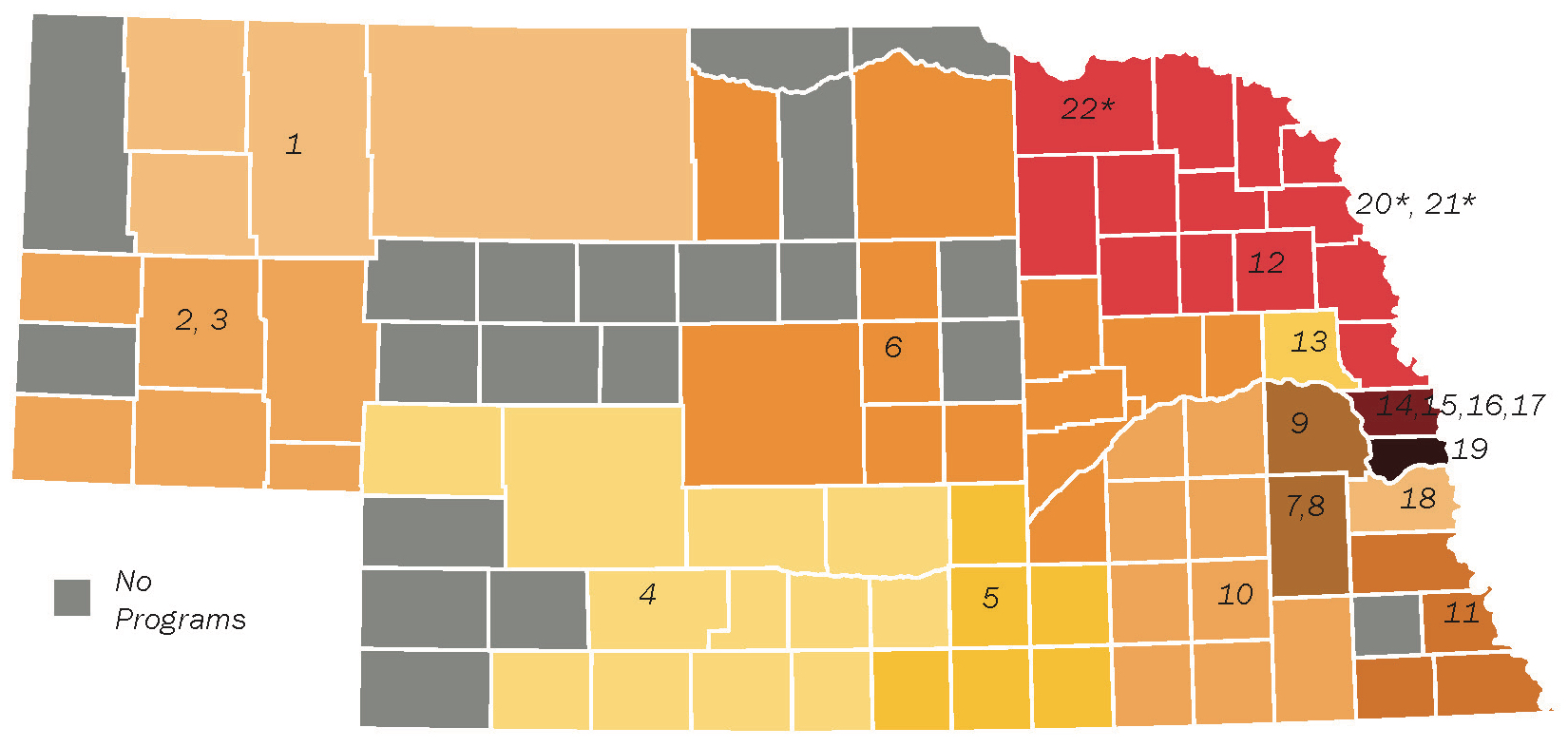
There were 16 Head Start programs and 12 Early Head Start Grantees – including 1 Early Head State Delegate program, and 1 Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Grantee.
| # | Grantee Name | Total Served | Early Head Start | Head Start |
| 1 | Northwest Community Action Partnership | 259 | 58 | 200 |
| 2 | Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Grantee | 65 | 65 | 0 |
| 3 | Educational Service Unit 13 | 350 | 52 | 298 |
| 4 | Community Action Partnership of Mid-Nebraska | 386 | 48 | 338 |
| 5 | Head Start Child & Family Development Program, Inc. | 496 | 162 | 334 |
| 6 | Central Nebraska Community Services, Inc. | 552 | 179 | 373 |
| 7/8/9 | Community Action Partnership of Lancaster and Saunders Counties and Delegates | 644 | 140 | 504 |
| 10 | Blue Valley Community Action Partnership | 329 | 90 | 239 |
| 11 | Southeast Nebraska Community Action | 156 | 0 | 156 |
| 12 | Northeast Nebraska Community Action Partnership | 417 | 0 | 417 |
| 13 | Midland Lutheran College/Dodge County Head Start | 94 | 0 | 94 |
| 14 | Salvation Army Early Head Start | 111 | 111 | 0 |
| 15/16 | Omaha Public Schools Head Start and Delegates | 1,013 | 0 | 1,013 |
| 17 | Nebraska Early Childhood Collaborative | 176 | 176 | 0 |
| 18 | Cass County Head Start/Plattsmouth Public School | 120 | 0 | 120 |
| 19 | Sarpy County Cooperative Head Start | 221 | 96 | 125 |
| 20* | Omaha Tribe of Nebraska | 101 | 0 | 101 |
| 21* | Santee Sioux Council Tribal Head Start | 90 | 0 | 90 |
| 22* | Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska | 35 | 0 | 35 |
Early Childhood Education
1,747
children served by Head Start/ Early Head Start have a primary language other than English.
957
children served by Head Start/Early Head Start were determined to have a disability.
School-based preschool (2014/15)
18,493
children enrolled in school-based preschool
- 15,253 (82.4%) in public schools
- 3,240 (17.5%) in nonpublic schools
Early Head Start/Head Start participants by race (2014/15)*
- American Indian or Alaska Native (2.9%)
- Asian or Pacific Islander (2.2%)
- Black/African American (12.2%)
- White (63.6%)
- 2+ races (7.7%)
- Some other race (6.4%)
- Unspecified (5.0%)
- American Indian or Alaska Native (2.9%)
- Asian or Pacific Islander (2.2%)
- Black/African American (12.2%)
- White (63.6%)
- 2+ races (7.7%)
- Some other race (6.4%)
- Unspecified (5.0%)
Source: Federal Head Start PIR System.
Public school pre-k enrollment (1998/99 - 2014/15)
Early Development Network (2014/15)
The Early Development Network (EDN) serves families with children born with disabilities.
1,375
children from birth to two were served by EDN.*
78
children ages three and older were served by EDN.*
*One-day count of children taken on October 1, 2014.
Sixpence (2014/15)
Sixpence serves children birth to age 3 who are at risk of failure in school and is funded through public and private dollars. There were 25 Sixpence programs in the state of Nebraska in the 2014/15 program year serving:
- 804 families
- 98 pregnant moms
- 871 children
Child Care
Children need a safe environment while their parents work. Ensuring that caregivers are licensed is an important first step toward keeping children safe. This data shows counties with and without adequate licensed child care capacity.
Capacity of licensed child care facilities per 100 children 5 & under with all available parents working, by county (2015)
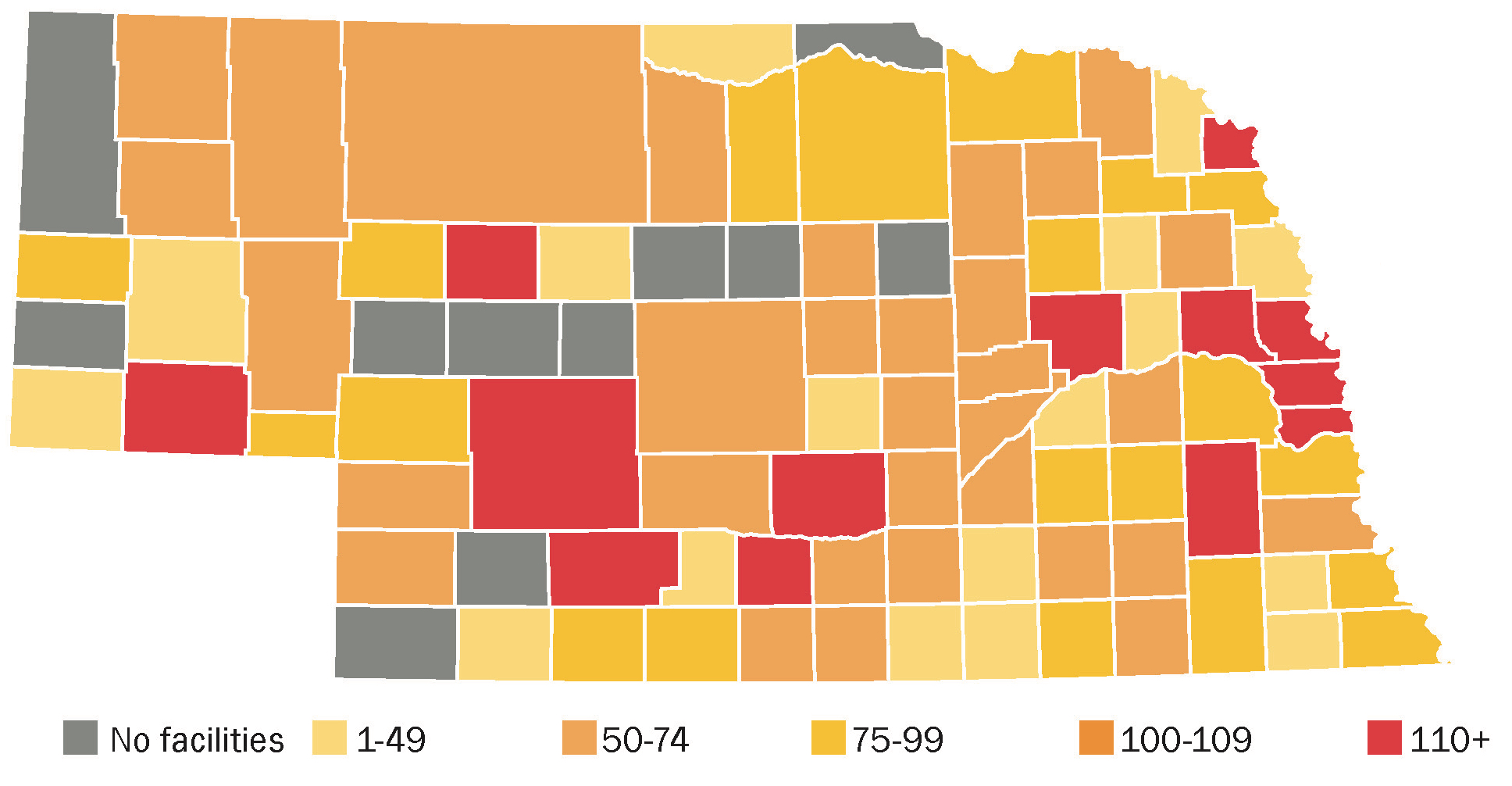
Licensed child care facilities
3,385 Total child care facilities
113,735 Total capacity
Annual child care costs (2015)
| Center-based care | |
| Infant | $9,043 |
| 4-year-old | $7,935 |
| School-age | $6,749 |
| Home-based care | |
| Infant | $7,104 |
| 4-year-old | $6,551 |
| School-age | $6,215 |
Child care subsidies (SFY 2015)
- There were 30,450 children in Nebraska who received child care subsidies in SFY 2015, for an average annual payment per child of $2,948. 3,952 children were in the care of a license-exempt facility.
- An average of 16,966 children received a subsidy each month, for an average monthly payment per child of $245.70.* 8,528 were below school-age, and 11,922 were school-age.
- 19,889 children receiving a subsidy were from a family living below 100% of the Federal Poverty Line (FPL), b were from families between 100%-130% FPL and 5,181 were TANF transition.
- The total state and federal funds spent for Child Care Subprogram 44, which includes child care subsidies, was $89,780,310.
QRIS
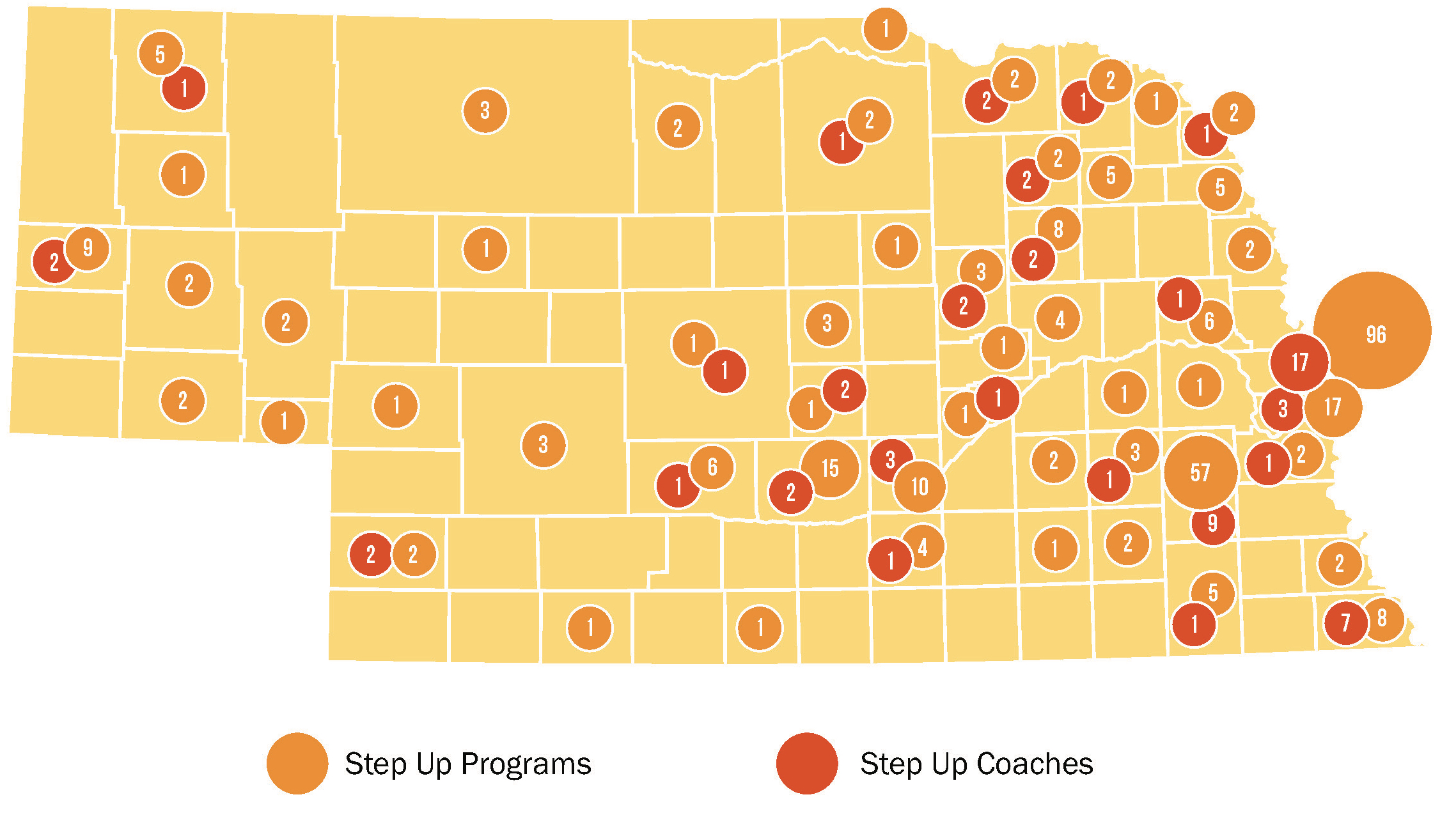
Nebraska Step Up to Quality is an Early Childhood Quality Rating and Improvement System (QRIS), passed by the Nebraska Legislature in 2013. The primary goal of Nebraska Step Up to Quality is to improve early care and education quality and increase positive outcomes for young children. This is done through informing parents about quality early care and education programs in understandable and measurable ways. In addition, it improves teacher and director effectiveness through training and professional development, formal education, and coaching. It also emphasizes strengthening the understanding and use of standards, assessment processes, and using data to improve quality.
As of 12/31/2015, Nebraska had
234 Step Up to Quality Programs
Nebraska Step Up to Quality program providers by step (12/31/2015)
70 Providers – Step 1: The program has completed the application to participate in Step Up to Quality, staff members have submitted a professional record, and the program’s director completes orientation.
19 Providers – Step 2: The program director completes several trainings related to safety, child health, and early learning and management as well as several self assessments related to child development knowledge.
22 Providers – Steps 3-5: Programs that are at Step 2 can begin earning points to reach Step 3 or higher. Points are earned through additional training and professional development, environment, quality of instruction and curriculum, measurable child outcomes, family and community partnership engagement, and program management.
Nebraska Step Up to Quality programs and coaches by county (as of 11/18/2016)
349,925 children were enrolled in public or nonpublic school in 2014/15.
Student Characteristics
138,868 public and nonpublic students were eligible for free and reduced meals in 2014/15.
| MEAL PROGRAM PARTICIPATION | |
| Breakfast | Lunch |
| 265 districts 940 sites |
381 districts 1,148 sites |
| COMMUNITY ELIGIBILITY (2014/15)* | ||
| Schools | Children | |
| Eligible | 111 | 43,594 |
| Served | 8 | 2,228 |
*Number of children eligible for the Community Eligibility Program is based on proxy data.
School membership by grade (2014/15)
Percentage of public and nonpublic students eligible for free and reduced school meals (2005/06 - 2014/15)
There were 276 Summer Food Participation sites in 2015 serving an average of 35,472 meals daily.
14.7% of students were classified as Special Education (2014/15).
14.5% of students were classified as High Ability Learners (2014/15).
Public school cost per pupil in 2015 dollars (2004/05 - 2014/15)
Rate of school mobility per 1,000 public school students (2004/05 - 2014/15)
School Mobility is a measure of how many students are transferring in and out of school within a school year. Higher school mobility is correlated with lower achievement.
Rate of home schooled students per 1,000 students (2004/05 - 2014/15)
Percentage of students who were English language learners (2004/05 - 2014/15)
Test Scores - Reading
Reading is a fundamental skill that affects learning experiences and school performance of children and teens. The ability to read proficiently translates to a greater likelihood of performing well in other subjects. Children with lower reading achievement are less likely to be engaged in the classroom, graduate high school, and attend college.
3rd Grade (2014/15)
82%
of children overall read proficiently
73%
of low-income children read proficiently
8th Grade (2014/15)
79%
of children overall read proficiently
66%
of low-income children read proficiently
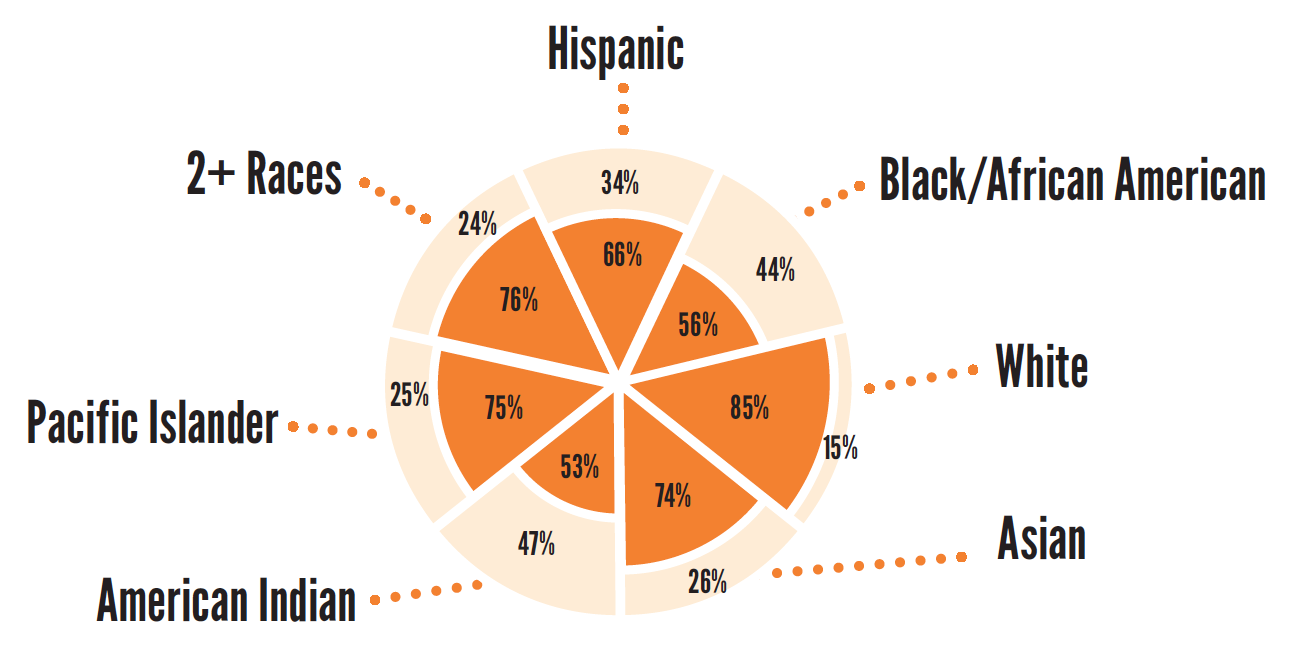
11th Grade (2014/15)
69%
of children overall read proficiently
53%
of low-income children read proficiently
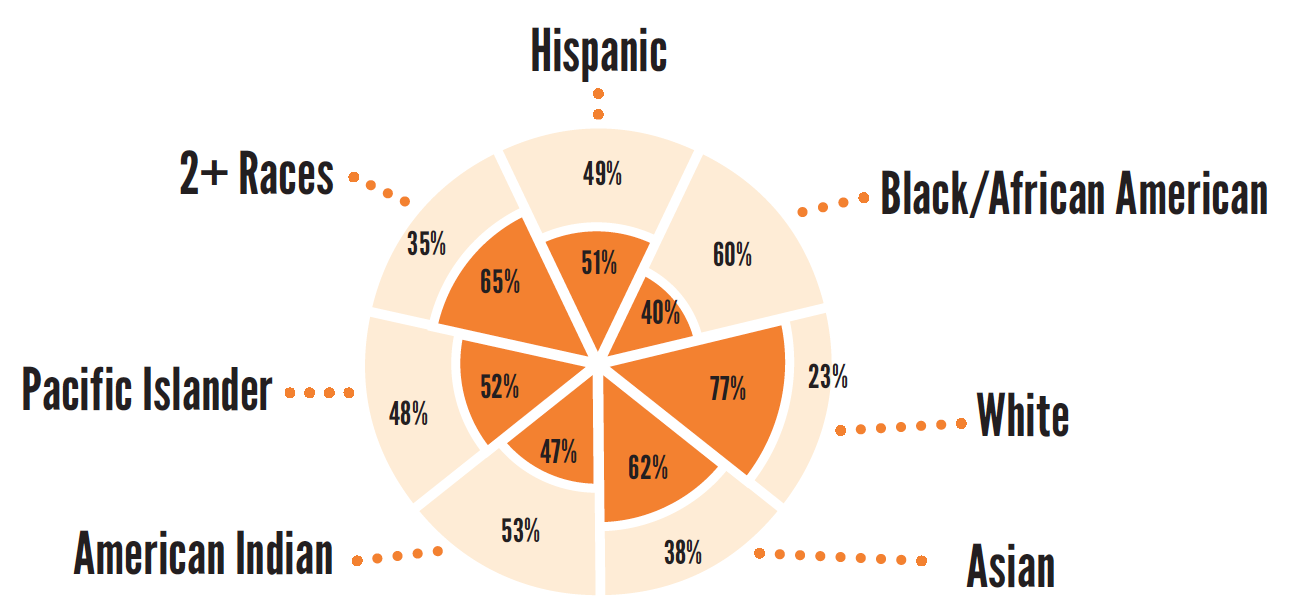
Test Scores - Math
Math skills are essential for functioning in everyday life, as well as for future success in our increasingly technical work environment. Students who take higher courses in mathematics are more likely to attend and complete college. Those with limited math skills are more likely to find it difficult to function in everyday society and have lower levels of employability.
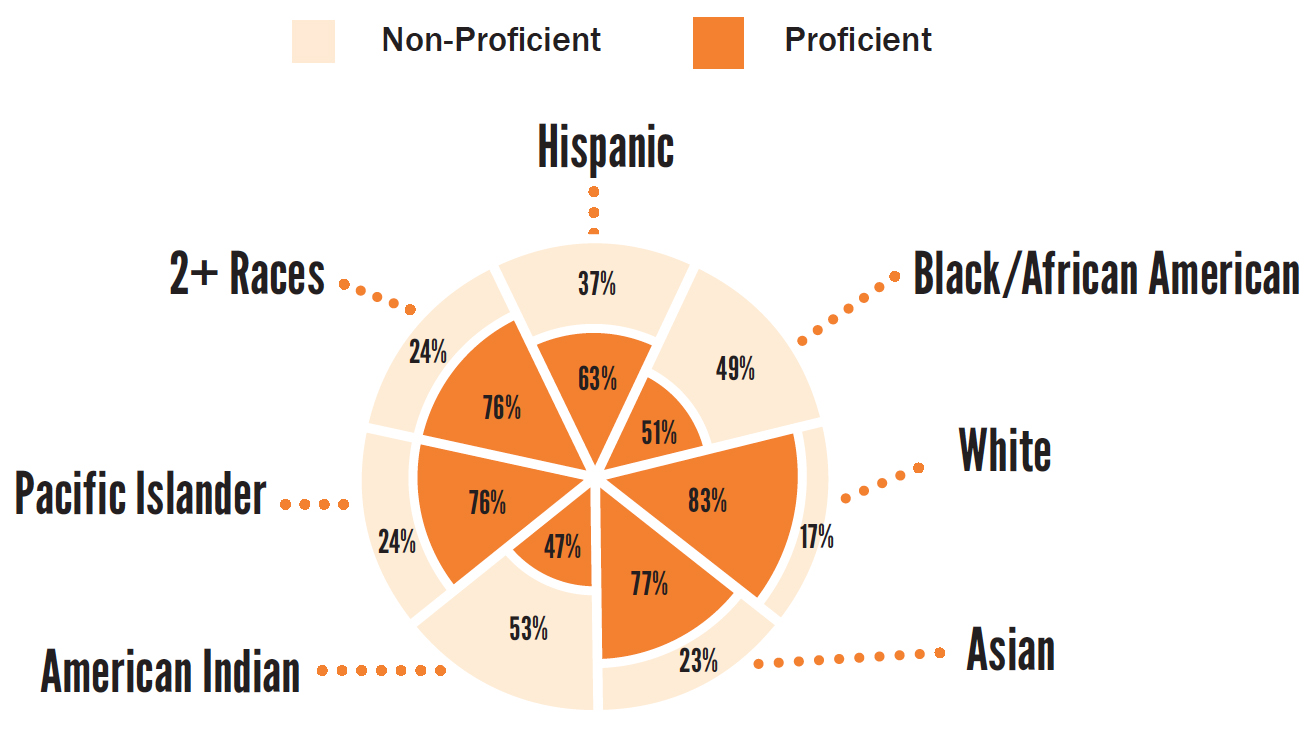
5th Grade (2014/15)
76%
of children overall are proficient in math
64%
of low-income children are proficient in math
8th Grade (2014/15)
68%
of children overall are proficient in math
51%
of low-income children are proficient in math
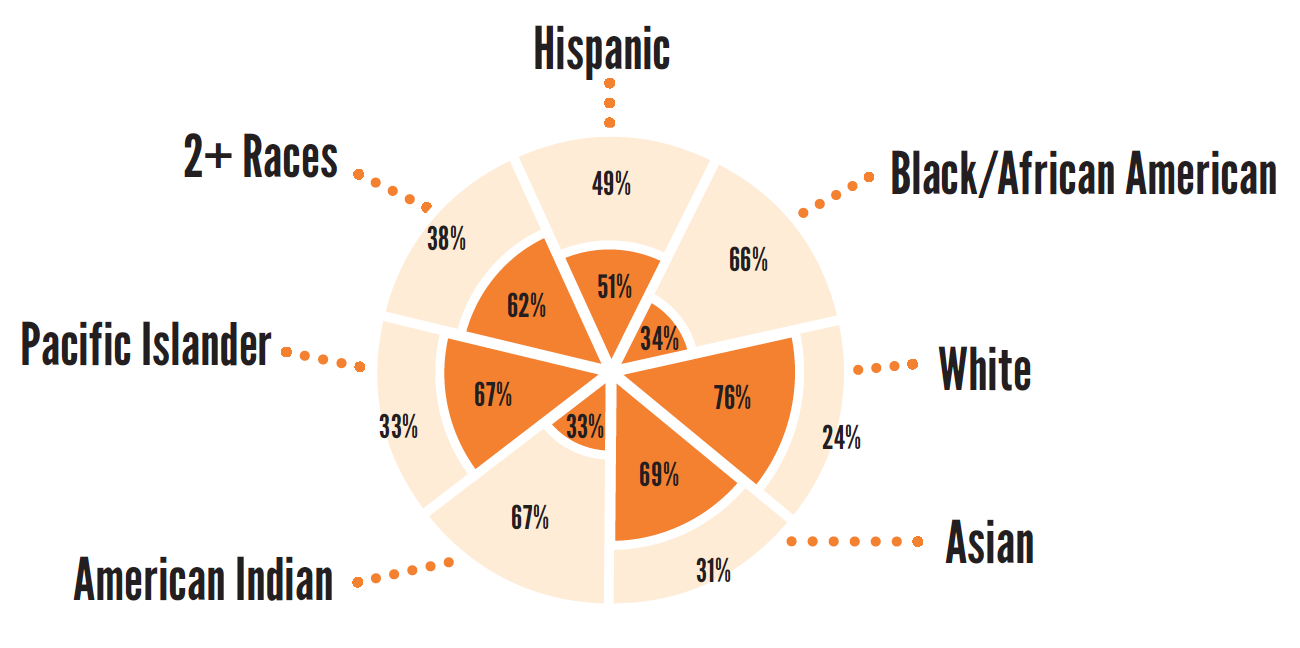
11th Grade (2014/15)
61%
of children overall are proficient in math
42%
of low-income children are proficient in math
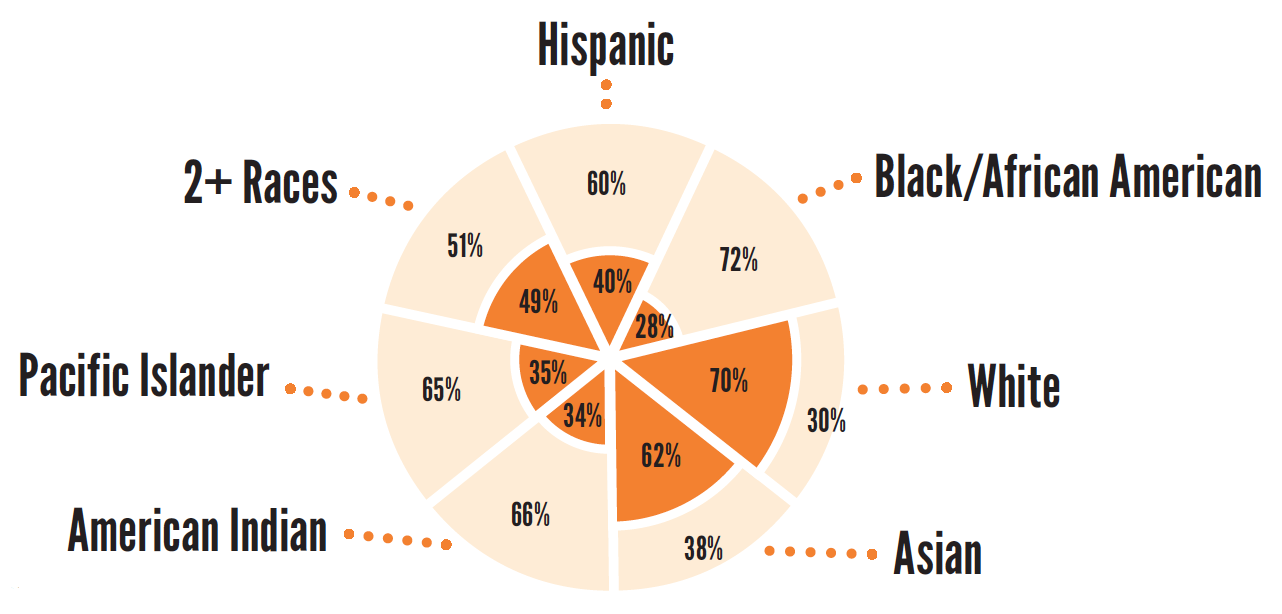
Test Scores - Science
Proficiency in science helps prepare students to go on to highly skilled professions. Having a strong foundation in the sciences allows students to work in today’s high demand fields. Students with a greater understanding of sciences learn how to better protect the environment and increase the health and security of people throughout the world.
5th Grade (2014/15)
73%
of children overall are proficient in science
59%
of low-income children are proficient in science
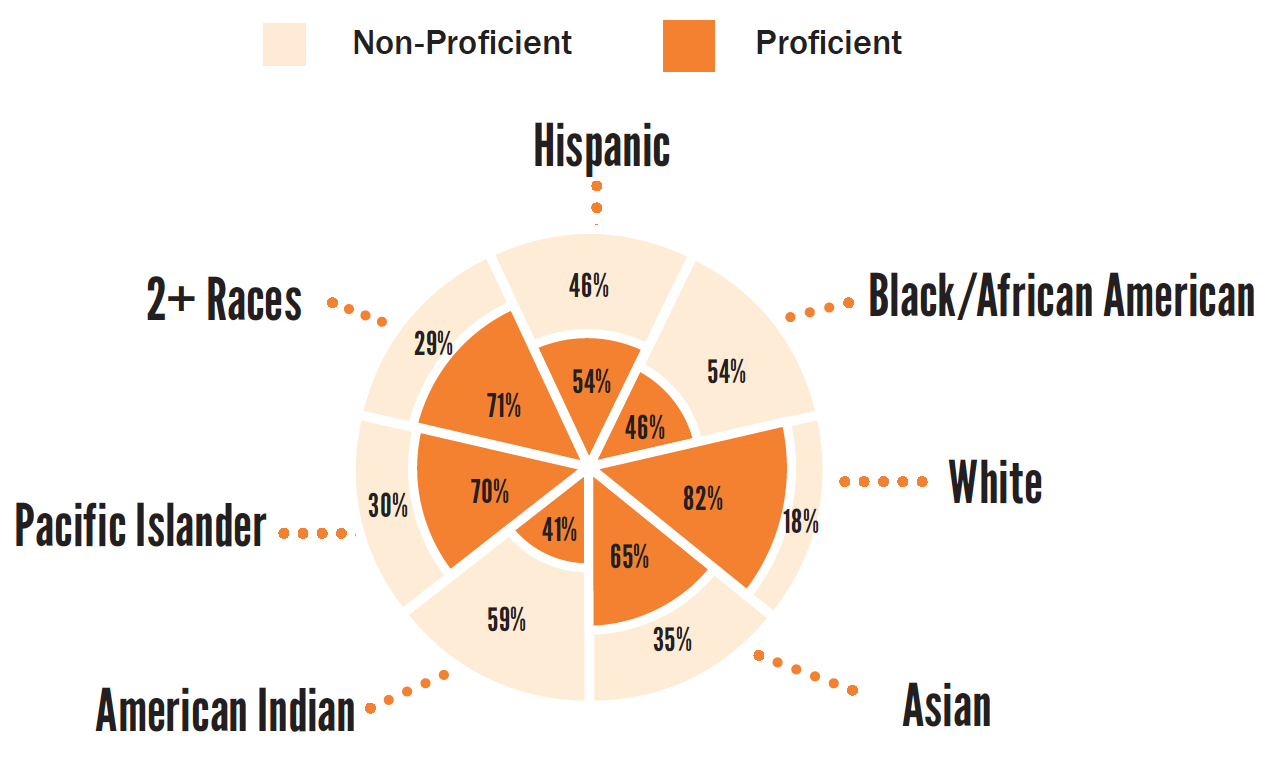
8th Grade (2014/15)
70%
of children overall are proficient in science
53%
of low-income children are proficient in science
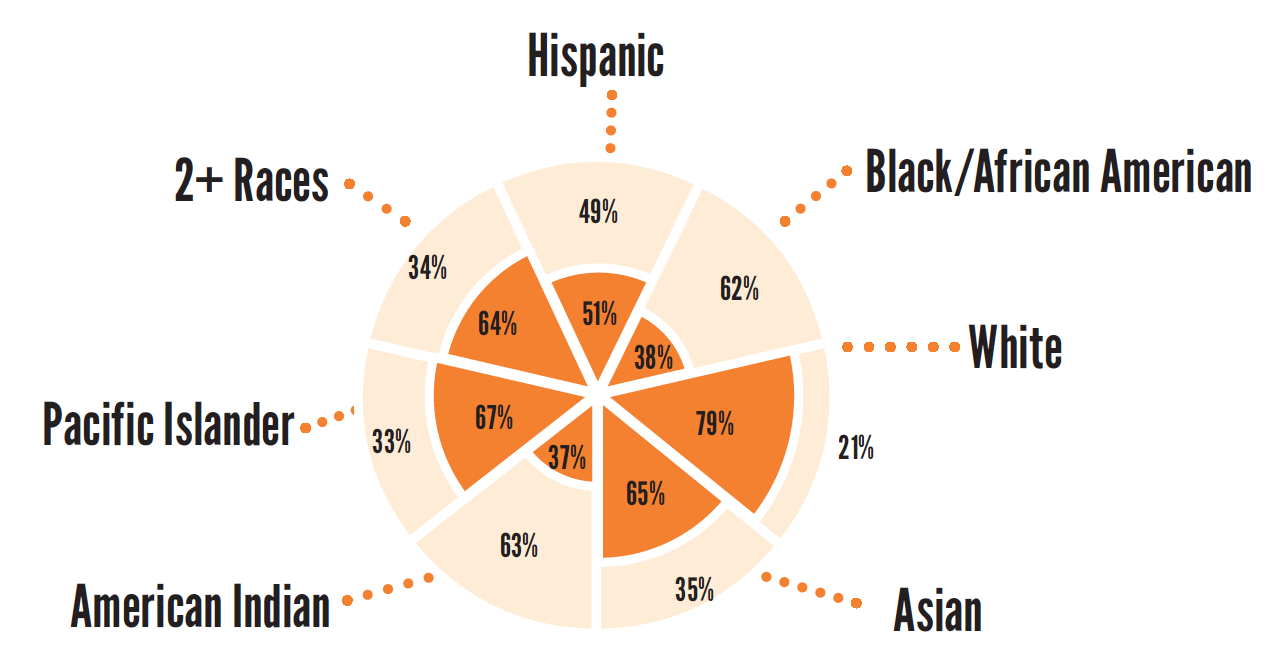
11th Grade (2014/15)
73%
of children overall are proficient in science
56%
of low-income children are proficient in science
Absences
Children need to be in school to achieve educational success and all the positive life outcomes that go with it. Too often, children are pushed out of the school system through suspensions, expulsions, and referrals to the court system. The cumulative sum of these practices, often referred to as “the school to prison pipeline,” has been shown to have a negative impact on students, schools, and academic achievement. When a student is suspended, they become less likely to graduate on time and more likely to repeat a grade, drop out without earning a diploma, and become involved with the juvenile justice system. Studies have also shown that schools with a higher reliance on school exclusion as a form of discipline actually score lower on academic achievement tests, even when controlling for socioeconomic and demographic factors. Policies that keep kids in the classroom produce better results for students, schools, and our communities as a whole.
792 (0.24%) students in public and (2014/15) nonpublic schools were EXPELLED during the 2014/15 school year.
13,326 (4.0%) students in public and nonpublic schools were SUSPENDED during the 2014/15 school year.
1,550 public and nonpublic students dropped out in 2014/15.
Public school absences (2014/15)
57,759
(17.4%) students were absent
10-19 days
12,073
(3.6%) students were absent
20-29 days
9,095
(2.7%) students were absent
30+ days
Graduation & Career
76% of graduates in 2012/13 enrolled in college by 10/15/2014.1
18,347 students took the ACT during the 2014/15 school year with average composite score of 21.5 (21.0 nationally).1
18,000 (10%) of young adults age 18-24 were not attending school, not working, and had no degree beyond high school.2
93,000 (49%) of young adults age 18-24 were enrolled in or completed college.2
6,000 (6%) of teens 16-19 were not in school and not working.2
8,832 students were enrolled in a career academy or dual credit courses in 2014/15.1
2. U.S. Census Bureau, 2014 American Community Survey 5-year estimates.
22,912
students completed high school in 2014/15.
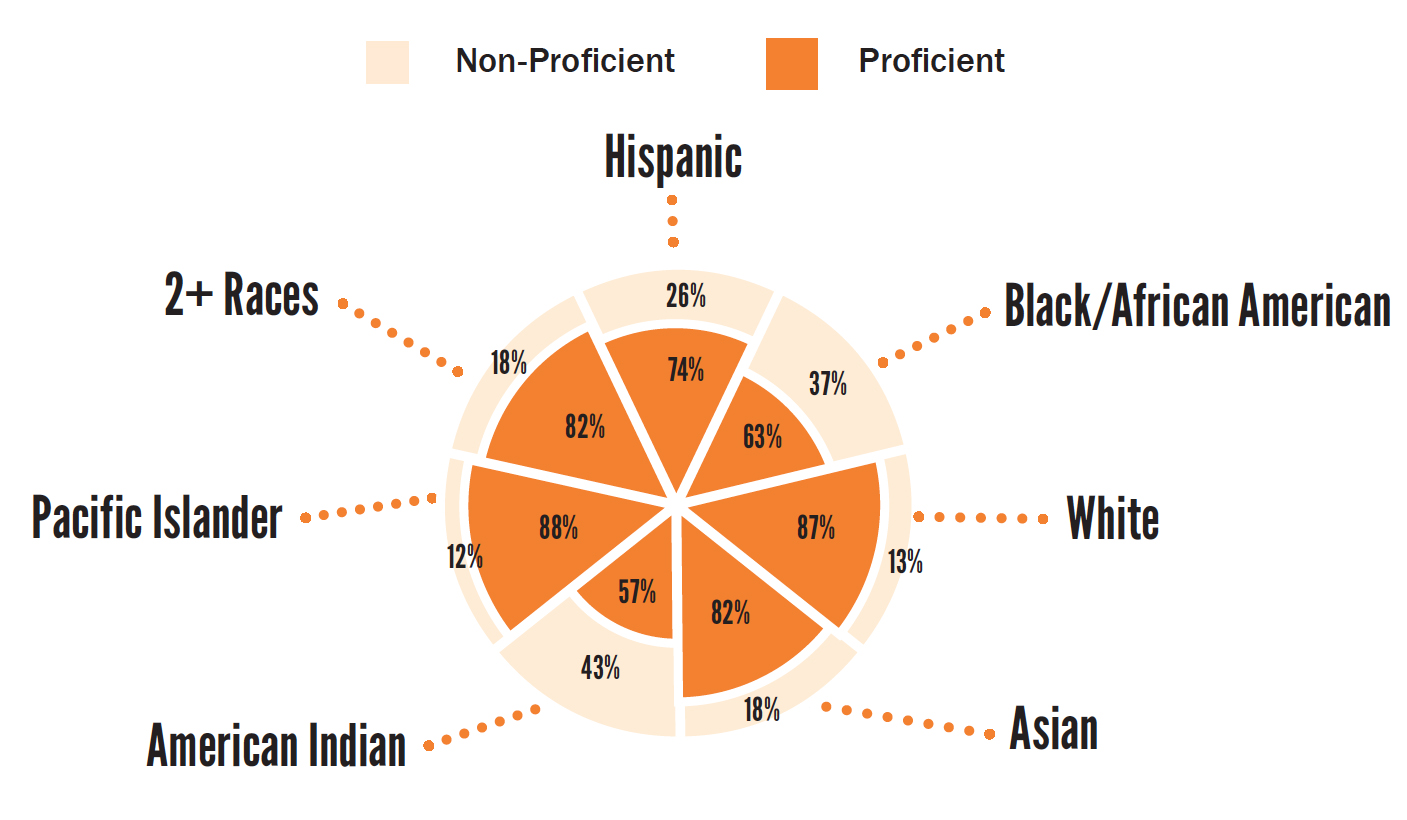
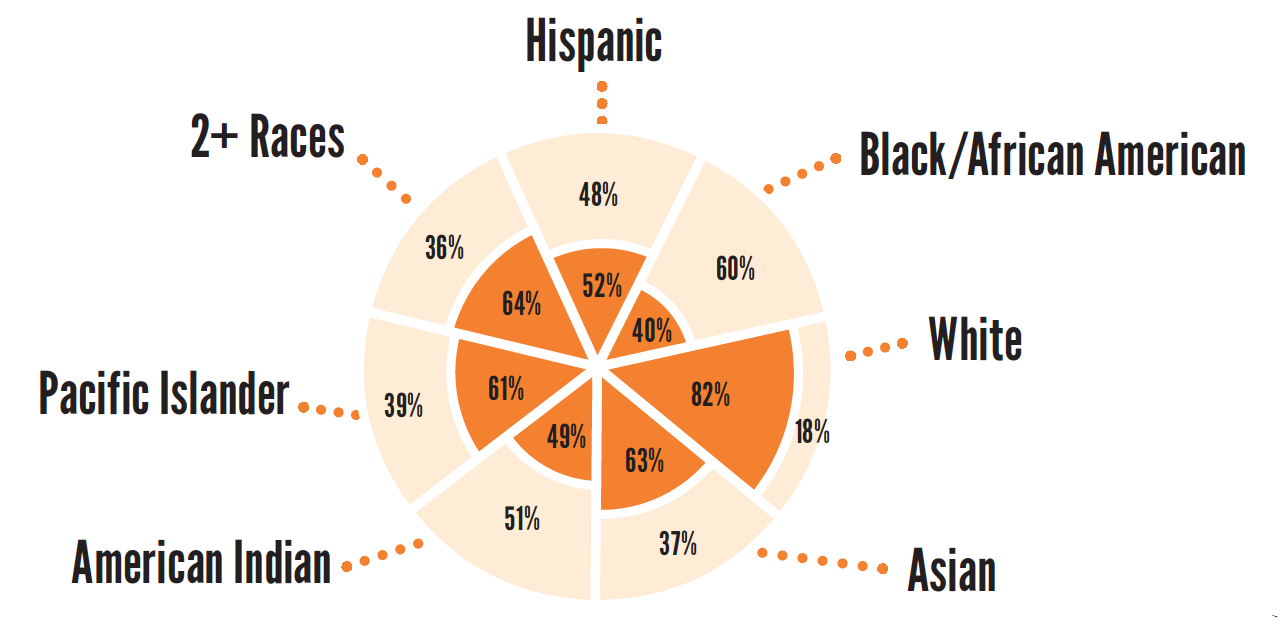
2015 cohort four-year graduation rates by student demographics
91.8%
2014 extended five-year graduation rate,*
an increase from 89.7% from the 2014 cohort four-year graduation rate.
Source: Nebraska Department of Education.

