Keeping our children and youth safe is essential to their healthy development. Youth should be held accountable for their actions in developmentally appropriate ways that promote community safety and allow them to grow into responsible citizens. When youth act out they should be held accountable primarily by families, schools, and communities, avoiding contact with the juvenile justice system if at all possible. Youth entering and in the juvenile justice system are entitled to be safe and their rights must be respected. Retaining strong connections to family, community, and culture help youth thrive within the system. The juvenile justice system should be rehabilitative in nature and designed specifically for youth.
Arrests
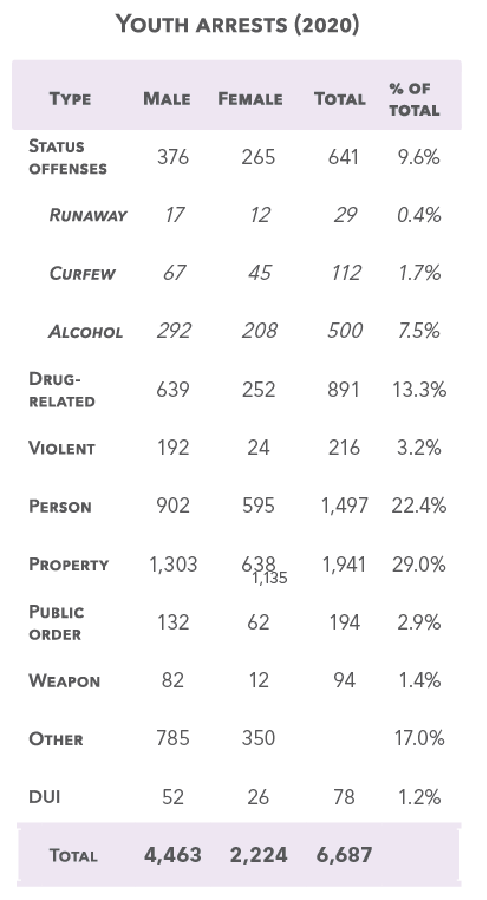
Status offenses
“Status offenses” are non-criminal behaviors, like skipping school, that could not be charged but for the “status” of being a minor.
6,687 youths were arrested in 2020.
The most common, 29.0%, were property crimes.
Number of youths arrested (2010-2020)
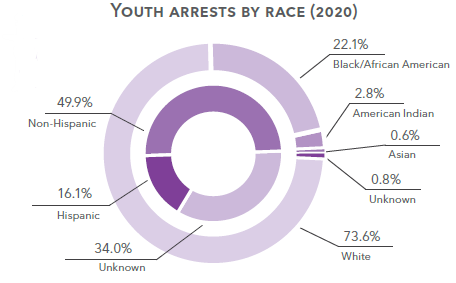
Disproportionate Minority Contact
Disproportionate minority contact (DMC)
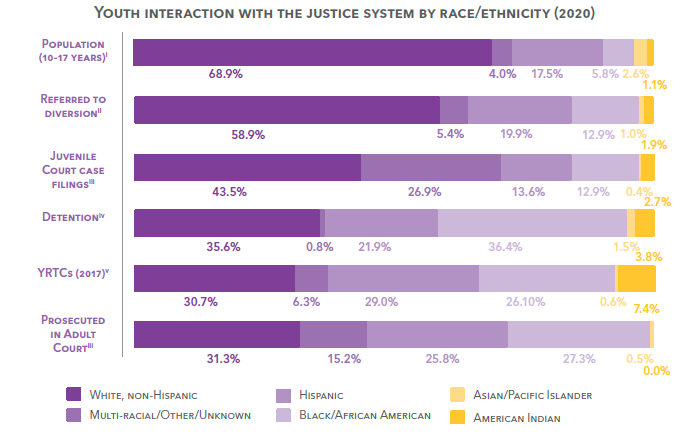
Despite the promise of equal protection under the law, national research shows that youth of color are overrepresented in the juvenile justice system. This overrepresentation often is a product of decisions made at early points of contact with the juvenile justice system. Where racial differences are found to exist, they tend to accumulate as youth are processed deeper into the system.1
Unfortunately, our juvenile justice system lacks uniform ways of collecting data on race and ethnicity. Although disparities exist across system points, different agencies have different ways of counting Hispanic youth in particular. Additional information on the race and ethnicity of youth arrested, on probation, and in adult prison are available elsewhere in this section.
ii. Nebraska Crime Commission, Juvenile Diversion 2020 Annual Report.
iii. Administrative Office of the Courts & Probation, Nebraska Juvenile Justice System Annual Report 2020.
iv. Analysis based on data from individual facilities including Lancaster County Detention Center, Northeast Nebraska Juvenile Services, Douglas County Youth Center, and the Patrick J. Thomas Juvenile Justice Center.
v. Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Juvenile Services Annual Legislative Report, SFY 2021.
*Data is input by clerks across the state and may not be well standardized. This may account for the large variance in the “multiracial/other/unknown” category.
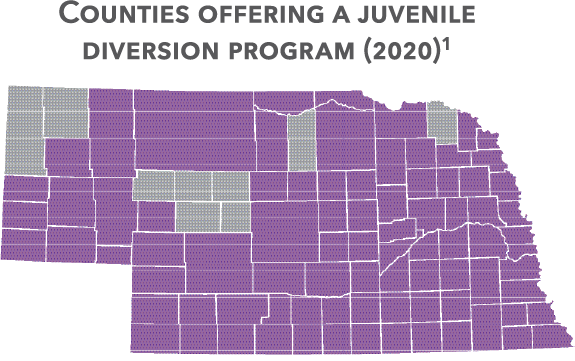
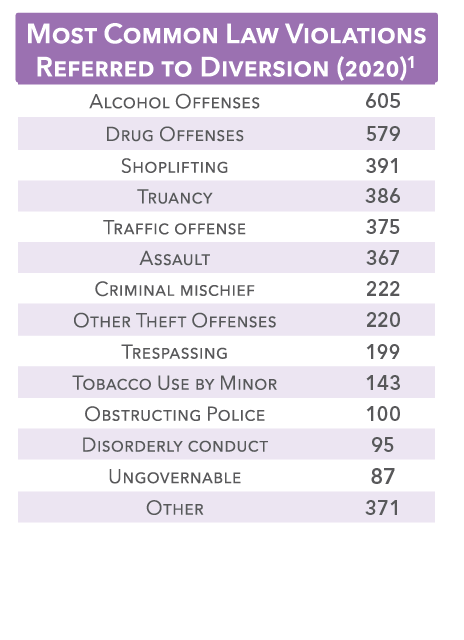
Pre-Trial Diversion
Juvenile diversion program
Pretrial diversion programs are based on the belief that many juvenile cases are better handled outside the courthouse doors. These voluntary programs are designed to provide eligible youth an opportunity to demonstrate rehabilitation and make things right with the community, while reducing the cost and burden to taxpayers and courts that come with formal charges being filed. By successfully completing his or her diversion plan, a minor has the opportunity to avoid formal charges in the court and get all record of the matter sealed. By diverting these cases from the court system, counties save significant dollars, making successful diversion programs a win-win.
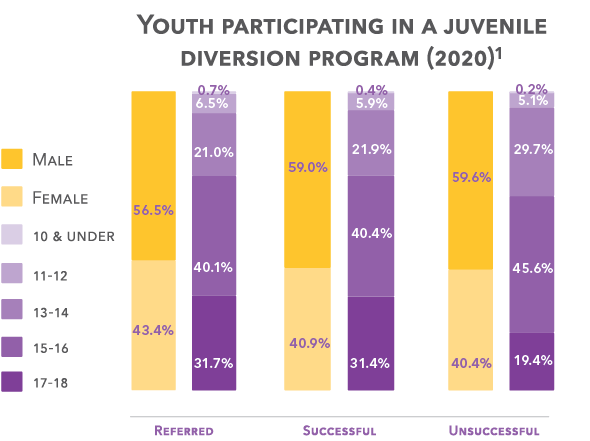
3,003
youths were referred to the diversion program. 1
489
of those referred did not participate.1
2,309
youths successfully completed diversion.1
428
youth did not complete diversion successfully and were discharged for failing to comply or for a new law violation. 1
84
counties participated in the diversion program.1
Community-Based Juvenile Services Aid Program (2020) 2
227 programs in 72 counties and 1 tribe were funded through the Community-Based Juvenile Services Aid Program in Fiscal Year 2019/20.
- 179 Direct Intervention
- 28 Prevention/Promotion Interventions
- 12 Direct Service Programs
- 36 System Improvement Programs.
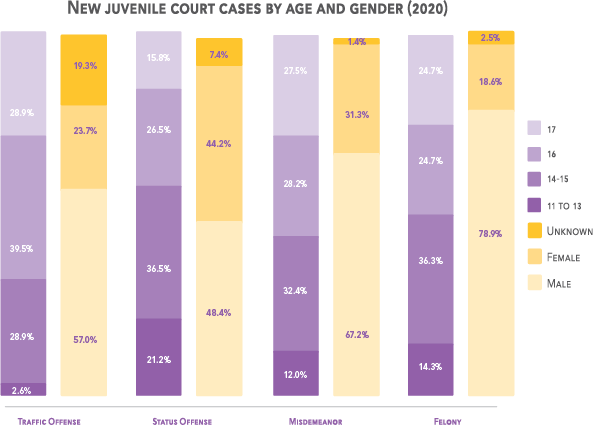
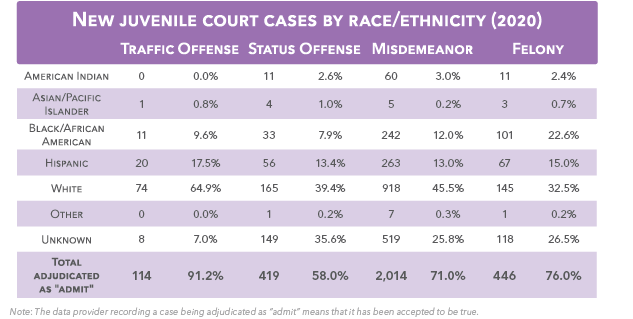
Juvenile Court Cases
Access to counsel
Juvenile access to counsel
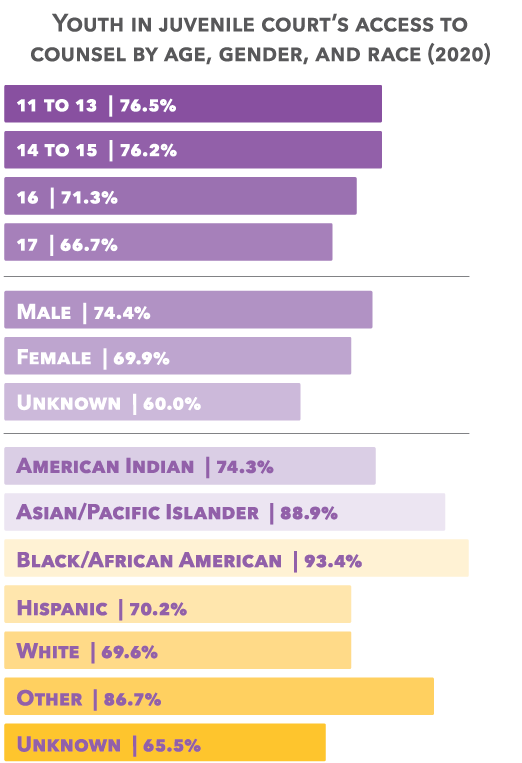
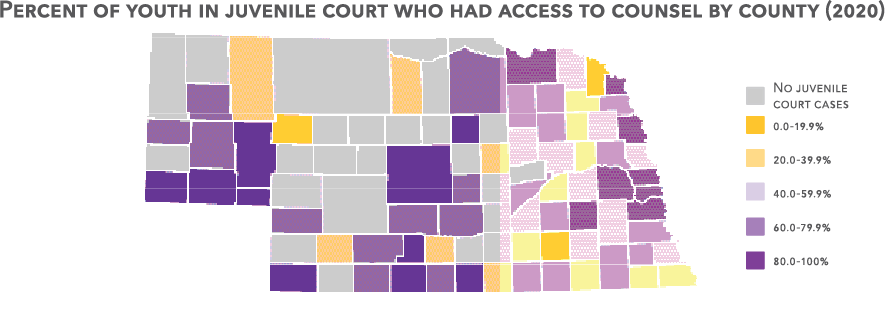
Having an attorney present during proceedings in the juvenile justice system is not only important for youth, but a guaranteed constitutional right. The right to counsel is also enshrined in Nebraska statute 43-272(1). The law is meant to protect children at every stage of legal proceedings, and requires the court to advise youth, along with their parents, of their right to an attorney and that legal counsel can be provided at no cost if they are unable to afford it. Unfortunately, all too frequently youth are not accessing this important protection.
40.1% of children in adult criminal court had an attorney in 2020.
72.6% of children in juvenile court had an attorney in 2020.
Probation

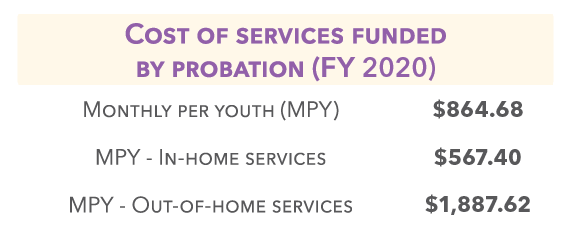
In 2020, 3,943 youths were supervised on probation –
• 678 had felony offenses
• 2,710 had misdemeanor, infraction, traffic, or city ordinance offenses
• 555 had status offenses
• 2,404 were discharged


Youth in out-of-home care
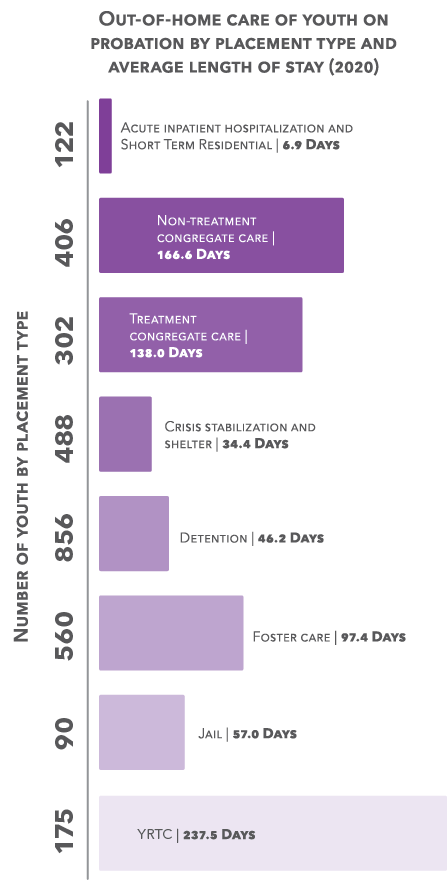
1,382 youth supervised on probation were placed in out-of-home care. The mean length of time in out-ofhome care was 2.9 months.
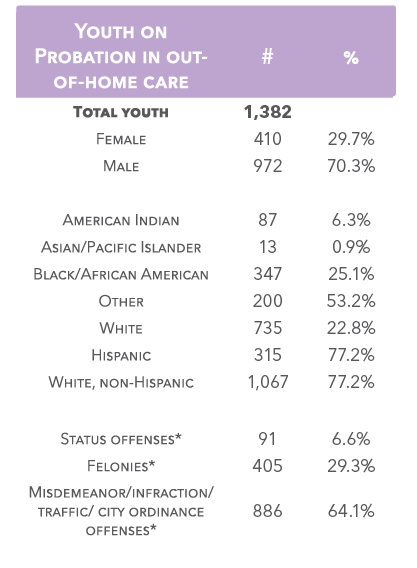
*If a youth had an offense in more than one adjudication type they will be counted by the youth’s highest or most serious offense.
Detention
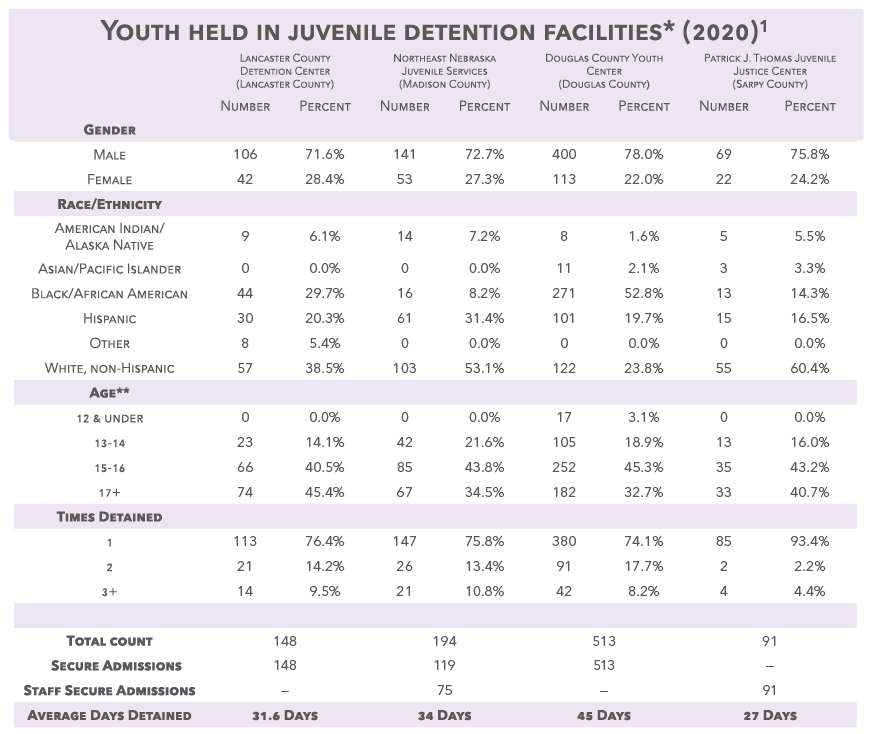
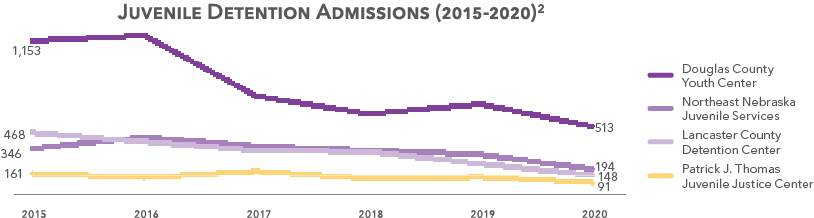
1. Individual detention centers.
2. Kids Count, 2020.
*Includes secure and staff secure detention.
** For Lancaster County Detention Center and Douglas County Youth Center if the same youth is admitted under different ages during the year, they will count under each age group.
YRTCs & room confinement
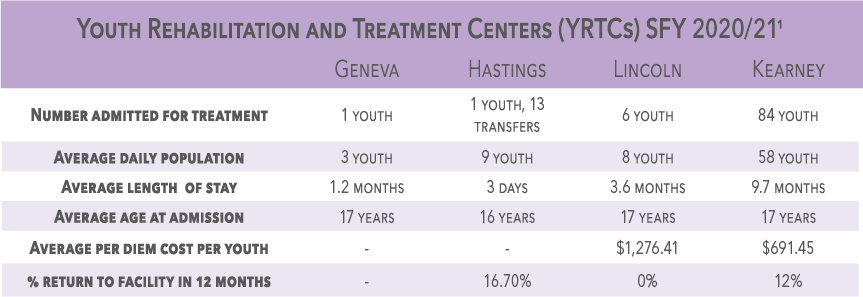
YRTC admissions (2010-2019)1
- Males
- Females
- Males
- Females
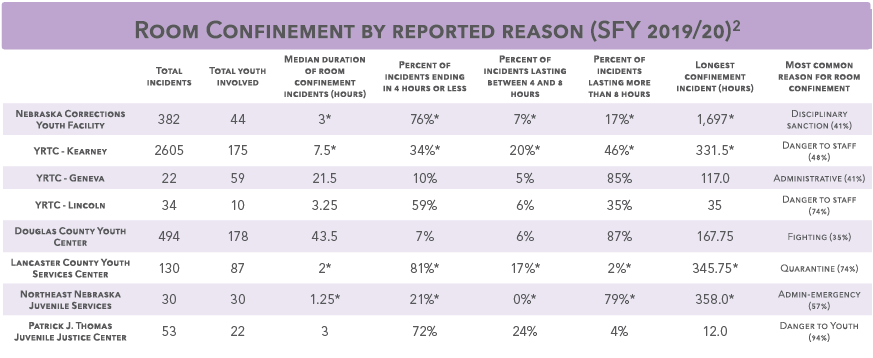
Research associates room confinement with serious consequences for mental and physical health including: – “Increased risk of self-harm and suicidal ideation; – Greater anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, paranoia, and aggression; – Exacerbation of the on-set of pre-existing mental illness and trauma symptoms; and, – Increased risk of cardiovascular related health problems.”³ Regulations, policies, and practices on when, how, and why juvenile room confinement is used differ among types of facilities. Room confinement should be used as the absolute last resort and only in cases of threats of safety to the individual or other residents and only after other interventions have failed. Room confinement should be time limited; the youth should be released as soon as they are safely able and should never last longer than 24 hours. During confinement, the youth should be closely monitored and seen by mental health professionals. All instances of room confinement should be recorded and reviewed.²
* Data includes room confinement resulting from Medical Quarantine incidents due to COVID-19 during the 4th quarter of this fiscal year.
1. Office of Juvenile Services, Annual Legislative Report SFY 2021.; Kids Count, 2020.
2. Office of Inspector General of Nebraska Child Welfare, Juvenile Room Confinement in Nebraska, 2019-20 Annual Report.
3.Haney, C. The Psychological Impact of Incarceration on Post-prison Adjustment. Prison to Home: The Effect of Incarceration and Reentry on Children, Families, and Communities, 2001.
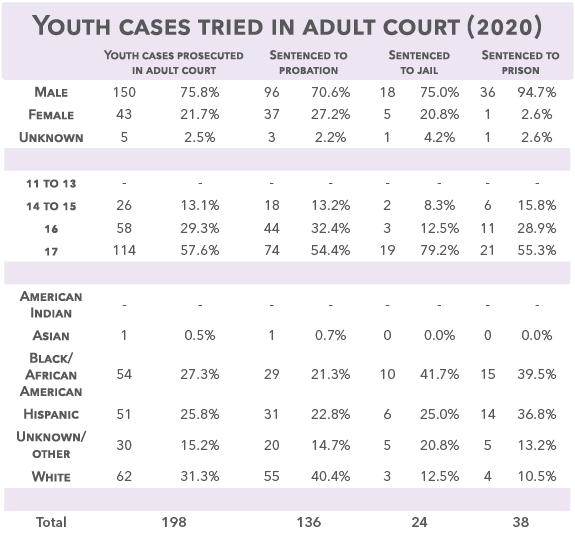
Youth Treated as Adults
An age-appropriate response
Research consistently indicates that treating children as adults neither acts as a deterrent, nor does it prevent crime or reduce violence – instead, prosecution in adult court exposes youth to more risks, delays or prevents treatment, and can burden them with permanent records which may act as barriers to future education and employment opportunities. Nebraska law requires that all children age 17 or younger charged with a misdemeanor or low-level felony must have their cases originate in juvenile court. This means that many more children are now receiving the benefit of speedy access to treatment services, a developmentally-appropriate court process aimed at rehabilitation, and the potential to have their records sealed to set them up for a brighter future.
In 2020, 198 youth cases were prosecuted in Nebraska adult courts, down from 2,019 in 2014.
Of the 198 youth cases prosecuted in adult criminal court in 2020, 23% were traffic cases, 44% were misdemeanor cases, and 33% were felony cases.
A motion to transfer from juvenile court to adult court was requested in 55 cases and granted in 12.
Adult court had 75 motions to transfer to juvenile court filed, and 92 cases transferred to juvenile court.

Youth incarcerated in correctional facilities by race/ethnicity (2020)
- American Indian
- Black/African American
- Hispanic
- White
- American Indian
- Black/African American
- Hispanic
- White
Source: Nebraska Department of Correctional Services.

